JSON Parser
The JSON Parser processor parses JSON data embedded in a column and passes the extracted data to new columns in the output row. The processor passes the JSON data in the original column unchanged.
When you configure the JSON Parser processor, you specify the column that contains the JSON data. You determine whether the processor extracts all elements in the JSON data, or extracts specific elements. When you configure the processor to extract specific elements, you can optionally flatten arrays in the JSON data before extracting elements. When flattening an array, the processor produces multiple output rows from a single input row, one output row for each child element within the array.
For information about how Snowflake handles JSON data, see the Snowflake documentation.
Extracted Column Names
The JSON Parser processor uses the original element names for the extracted column names. You can optionally add a prefix to all extracted column names to avoid duplicate names.
When the processor extracts child elements from objects or arrays in the JSON data, the processor uses the following naming conventions to determine the name of each extracted column:
- Column names from objects
-
When extracting child elements from an object in the JSON data, the processor uses the following column naming convention:
<object name>_<column name>For example, if extracting elements from the following user object, the processor names the extracted columnsuser_IDanduser_name:{ "user": { "ID":23005, "name":"Marnee Gehosephat" } } - Column names from arrays
-
When extracting child elements from an array in the JSON data, the processor uses the following column naming convention:
<array name>_<position>For example, if extracting elements from the following items array, the processor names the extracted columnsitems_0,items_1, anditems_2:{ "items": [ "T-35089", "M-00352", "Q-11044" ] }
Extract All Elements
By default, the JSON Parser processor extracts all elements from the JSON data, recursively extracting all child elements inside objects or arrays and extracting all columns as Variant columns.
{
"items":
[
"T-35089",
"M-00352",
"Q-11044"
],
"transactionID":235253350,
"user":
{
"ID":23005,
"name":"Marnee Gehosephat"
}
}| transaction | items_0 | items_1 | items_2 | transactionID | user_ID | user_name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
{"items":["T-35089", "M-00352", "Q-11044"],
"transactionID":235253350, "user":{"ID":23005,"name":"Marnee
Gehosephat"}} |
"T-35089" |
"M-00352" |
"Q-11044" |
235253350 |
23005 |
"Marnee Gehosephat" |
Extract Objects and Arrays with JSON Data
When extracting all elements and you want to extract objects and arrays as single columns containing JSON data, clear the Recursive property when you configure the processor.
items and user elements as single columns
containing JSON data:| transaction | items | transactionID | user |
|---|---|---|---|
{"items":["T-35089", "M-00352", "Q-11044"],
"transactionID":235253350, "user":{"ID":23005,"name":"Marnee
Gehosephat"}} |
["T-35089", "M-00352", "Q-11044"] |
235253350 |
{"ID":23005,"name":"Marnee
Gehosephat"} |
Infer the Data Type
When extracting all elements, you can configure the processor to infer the data type based on the column value, rather than extracting all columns as Variant columns.
For example, if you configure the processor to extract the same data from the
transaction column, but select the Infer Data Type
property, the processor infers that the transactionID column
contains a number value, and extracts the column as a Number.
Extract Specific Elements
You can configure the JSON Parser processor to extract specific elements from the JSON data.
- Name/value pair
- To extract a name/value pair from JSON data, enter the column name.
- Object
- To extract a child element from an object, enter the path using the following format:
- Array
- To extract a child element from an array, enter the path using the following format:
For each element that you add, you can optionally select the data type to convert the column to. If you do not select a data type, the processor extracts all columns as Variant columns.
Flatten Arrays Before Extracting
By default when extracting specific elements and when an array includes child elements with a list of name/value pairs, the JSON Parser processor extracts each child element as a column containing a list of name/value pairs.
To extract each pair as a new column, configure the processor to flatten the array into a relational representation before extracting elements. When flattening an array, the processor produces multiple output rows from a single input row, one output row for each child element within the array. Each row includes all extracted columns along with one of the flattened child elements of the array.
- On the JSON tab, select the Flatten by Expression property.
- Specify the array to flatten in the Flatten By property.
- In the Elements to Extract property, add at least one element from the flattened array and select Extract from Value Column when Flattening for that element.
- As needed, add additional elements included in the JSON data but outside of the flattened array to pass those elements as columns to the output row. For these elements, clear Extract from Value Column when Flattening.
For more information about how Snowflake flattens JSON data, see the Snowflake documentation.
Example: Default Array Processing
contact.business array that includes child elements with a list
of name/value
pairs:{
name:
{ first: "John", last: "Smith"},
contact:
{ business:
[
{ type: "phone", content:"555-1234" },
{ type: "email", content:"j.smith@company.com" }
]
}
}To extract the array without flattening it, you configure the processor to extract
specific elements from the information column, and enter
contact.business[*] as the element to extract, as follows:
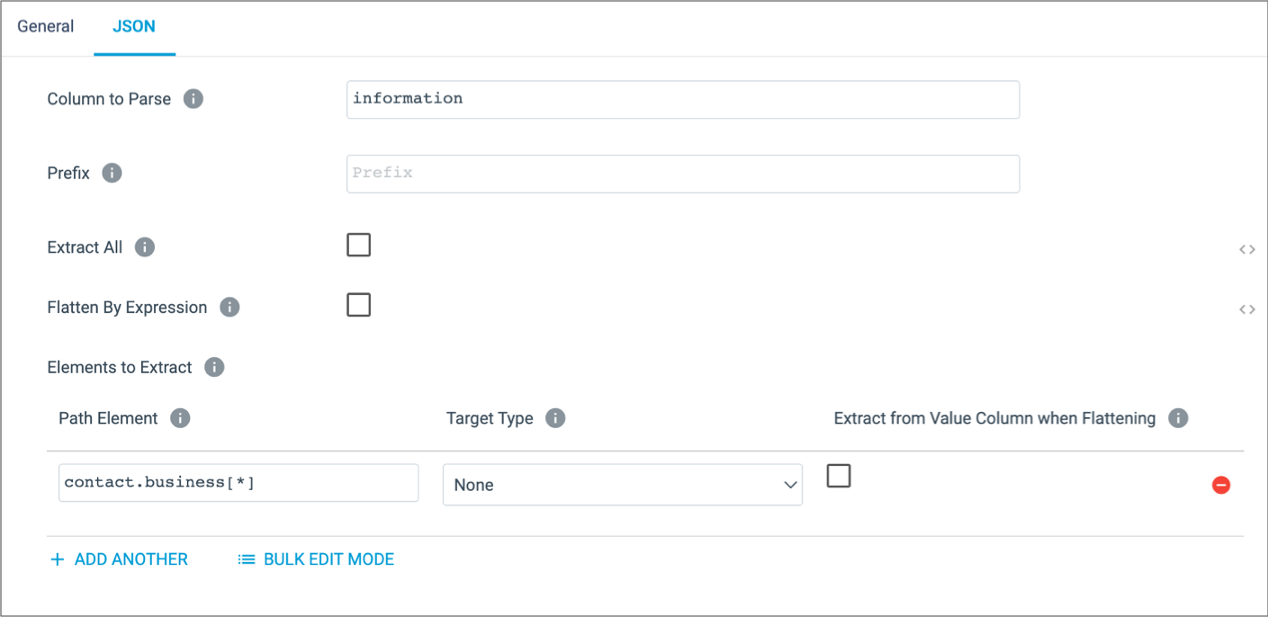
With this configuration, the processor generates the following output row, where each
element in the contact.business array is extracted as a column
containing a list of name/value pairs:
| information | contact_business_0 | contact_business_1 |
|---|---|---|
{ name: { first: "John", last: "Smith"}, contact: {
business:[ { type: "phone", content:"555-1234" }, { type:
"email", content:"j.smith@company.com" } ] }
} |
{"content":"555-1234","type":"phone"} |
{"content":"j.smith@company.com","type":"email"} |
Example: Flattening an Array
Instead of using the default processing, you decide to flatten the
contact.business array when you extract specific elements from
the information column. You also configure the processor to extract
the type and content elements from the flattened
array, and to extract the first and last name elements that are outside of the
array, as follows:
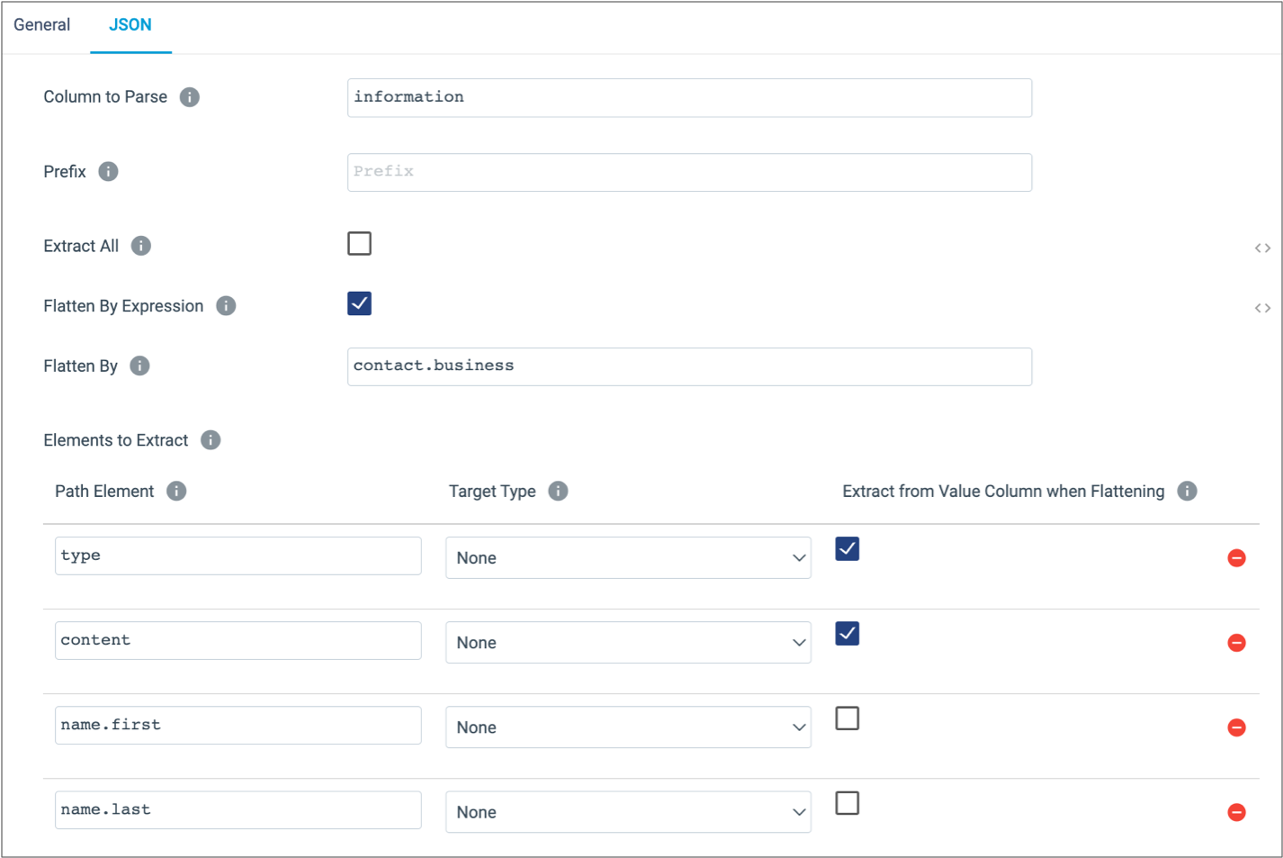
contact.business
array:| information | type | content | name_first | name_last |
|---|---|---|---|---|
{ name: { first: "John", last: "Smith"}, contact: {
business:[ { type: "phone", content:"555-1234" }, { type:
"email", content:"j.smith@company.com" } ] }
} |
"phone" |
"555-1234" |
"John" |
"Smith" |
{ name: { first: "John", last: "Smith"}, contact: {
business:[ { type: "phone", content:"555-1234" }, { type:
"email", content:"j.smith@company.com" } ] }
} |
"email" |
"j.smith@company.com" |
"John" |
"Smith" |
Configuring a JSON Parser Processor
Configure a JSON Parser processor to parse JSON data embedded in a column and pass the extracted data to new columns in the output row.
-
On the General tab, configure the following
properties:
General Property Description Name Stage name. Description Optional description. Cache Data Caches processed data. -
On the JSON tab, configure the following properties:
JSON Property Description Column to Parse Column that contains the JSON data. You can enter the column name or select a column from preview data. Prefix Optional prefix to add to extracted column names. Use to avoid duplicate column names.
Extract All Extracts all elements from the JSON data. Recursive Extracts all child elements from objects or arrays in the JSON data, creating a new column for each child element. When cleared, extracts objects and arrays as single columns containing JSON data. Available when extracting all elements.
Infer Data Types Infers the data type of each extracted column based on the column value. When cleared, the processor extracts all columns as Variant columns. Available when extracting all elements.
Flatten By Expression Flattens the data in an array into a relational representation before extracting elements. Flatten an array when you want to extract each element in the array, creating a new column for each child element. Important: You must add at least one element from the flattened array to the Elements to Extract property.Available when extracting specific elements.
Flatten By Array from the JSON data that you want to flatten. Available when flattening an array.
Elements to Extract Specific elements to extract from the JSON data. Define the path to the element. Optionally, in the Target Type column, select the data type to convert the column to. If no data type is selected, the processor extracts all columns as Variant columns.
When adding an element from a flattened array, select Extract from Value Column when Flattening. When adding an element outside of the flattened array, clear the property.
Using simple or bulk edit mode, click Add Another to define another element to extract.
Available when extracting specific elements.