Join
The Join processor joins related data from two inputs, generating rows that include data from both inputs. If you simply want to merge two or more sets of data into a single data flow, use the Union processor.
You can use the Join processor to join data from two different origins by connecting the Join processor to both origins. You can also use the Join processor to join two branches of data in your pipeline.
For example, you can use the processor immediately after two origins to merge that data. Now say you create a second branch in your pipeline to perform aggregate calculations. You can then use the Join processor to merge the results of the calculations with the other branch of data.
The Join processor can join data from two inputs. To join more than two inputs in a single pipeline, add additional Join processors to the pipeline.
When you configure the Join processor, you specify the type of join to perform and the join condition to use.
When the joined inputs have identical column names, the processor adds a
t1_ or t2_ prefix to the column name to avoid
duplicate names: t1_ for the left input and
t2_ for the right input. To remove or rename one of the columns, use a Column Remover or Column Renamer
processor downstream.
For example, if you configure the processor to join inputs that both include a column
named comments, the processor includes a t1_comments
column and a t2_comments column in the generated output. If you want to
keep both columns, you might use the Column Renamer processor to replace the
t1_ and t2_ prefixes with the originating table
names.
Join Types
- Inner - Returns rows that have matching values in both inputs.
- Cross - Returns the Cartesian product of two sets of data.
- Full outer - Returns all rows, including rows that have matching values in both inputs, and rows from either input that do not have a match.
- Left anti - Returns rows from the left input that do not have a match in the right input.
- Left outer - Returns rows from the left input, and matching rows from the right input.
- Left semi - Returns rows that have matching values in both inputs, but includes only the data from the left input.
- Right anti - Returns rows from the right input that do not have a match in the left input.
- Right outer - Returns rows from the right input, and matching rows from the left input.
In the pipeline canvas, the first input stream that you connect to the Join processor represents the left input. The second input stream that you connect to the processor represents the right input.
For example, in the following image, the customers input stream represents the left input because it was connected to the processor first. The orders input stream represents the right input because it was connected to the processor second.
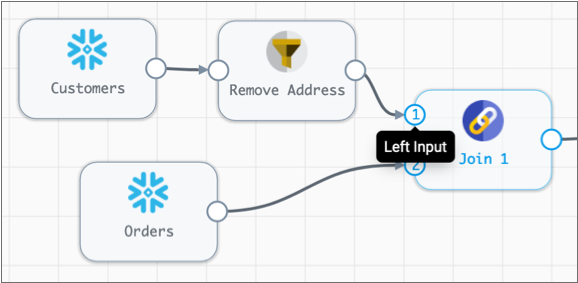
You can reorder the left and right inputs by selecting the processor to display the
pop-up menu, then clicking the Reorder icon: ![]() .
.
Join Type Examples
Let's look at an example for each join type. The examples join customer and order data
using matching values in the column named customer_id and the default
Columns to Join
On join condition.
Because the join column name is identical in both inputs, the processor adds a
t1_ or t2_ prefix to the column name in the
generated output. The processor uses t1_ for the left input and
t2_ for the right input.
The customer data is the left input and contains the following rows:
| customer_id | customer_name |
|---|---|
| 2 | Anna Smith |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo |
| 98 | Theo Barnes |
| customer_id | order_id | amount |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
| 342 | 1050945 | 126.05 |
Inner Join
An inner join returns rows that have matching values in both inputs.
When the Join processor performs an inner join on the sample data using Columns to Join On
as the join condition and customer_id for both join columns, the
processor produces the following output:
| t1_customer_id | customer_name | t2_customer_id | order_id | amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anna Smith | 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo | 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
Cross Join
A cross join returns the Cartesian product of two sets of data. A Cartesian product is the set of all possible ordered pairs between the two inputs.
When configuring the Join processor to perform a cross join, you do not specify a join condition.
| t1_customer_id | customer_name | t2_customer_id | order_id | amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anna Smith | 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 2 | Anna Smith | 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
| 2 | Anna Smith | 342 | 1050945 | 126.05 |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo | 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo | 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo | 342 | 1050945 | 126.05 |
| 98 | Theo Barnes | 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 98 | Theo Barnes | 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
| 98 | Theo Barnes | 342 | 1050945 | 126.05 |
Full Outer Join
A full outer join returns all rows, including rows that have matching values in both inputs and rows from either input that do not have a match.
customer_id for both join columns, the
processor produces the following output: | t1_customer_id | customer_name | t2_customer_id | order_id | amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anna Smith | 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo | 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
| 342 | 1050945 | 126.05 | ||
| 98 | Theo Barnes |
Left Anti Join
A left anti join returns rows from the left input that do not have a match in the right input.
customer_id for both join columns, the
processor produces the following output:| t1_customer_id | customer_name |
|---|---|
| 98 | Theo Barnes |
Left Outer Join
A left outer join returns rows from the left input, and matched rows from the right input.
customer_id for both join columns, the
processor produces the following output:| t1_customer_id | customer_name | t2_customer_id | order_id | amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anna Smith | 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo | 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
| 98 | Theo Barnes |
Left Semi Join
A left semi join returns rows that have matching values in both inputs, but does not include the merged data from both inputs. The results include only the data from the left input.
customer_id for both join columns, the
processor produces the following output:| t1_customer_id | customer_name |
|---|---|
| 2 | Anna Smith |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo |
Right Anti Join
A right anti join returns rows from the right input that do not have a match in the left input.
customer_id for both join columns, the
processor produces the following output:| t2_customer_id | order_id | amount |
|---|---|---|
| 342 | 1050945 | 126.05 |
Right Outer Join
A right outer join returns rows from the right input, and matched rows from the left input.
customer_id for both join columns, the
processor produces the following output:| t1_customer_id | customer_name | t2_customer_id | order_id | amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Anna Smith | 2 | 1075623 | 34.56 |
| 47 | Raquel Trujillo | 47 | 1076645 | 234.67 |
| 342 | 1050945 | 126.05 |
Join Conditions
- Columns to Join On property
- The Columns to Join On property enables specifying the join columns for each input. The specified columns can have identical or unique names. When the processor performs the join, it adds each set of join columns to the output, in addition to the other columns added for the join type.
- Join condition: Using
- The Using join condition also enables specifying join columns. However, you specify a single column name for both inputs, so the column names must be the same. When the processor performs the join, it adds only one of the join columns to the output, in addition to the other columns added for the join type.
- Join condition: On
- The On join condition enables you to define a custom condition for the join.
When defining the join condition, use prefixes when referencing the two sets
of data. The processor uses
t1_andt2_by default,t1_for the left input andt2_for the right input. If you specify custom prefixes, you must use them in the join condition.
Configuring a Join Processor
Configure a Join processor to join related data from two inputs and generate rows that include data from both inputs. If you simply want to merge two or more sets of data into a single data flow, use the Union processor.
-
On the General tab, configure the following
properties:
General Property Description Name Stage name. Description Optional description. Cache Data Caches processed data. -
On the Join tab, configure the following properties:
Join Property Description Join Type Type of join to perform. Define Join Condition Enables using the On or Using join condition. Leave clear to use the default Columns to Join On condition.
Join Command Join condition to use: - On
- Using
Available when Define Join Condition is enabled.
Join Condition Condition to use with the On join condition. Specify any valid Snowflake condition. Available with the On join command. Not available for Cross joins.
Input 1 Prefix Prefix for the first, or left, input. Use the specified prefix when defining the left input in the On join condition. The processor adds the prefix to columns from the left input when identical column names exist in the right input.
Default is
t1_.Available with the On join command.
Input 2 Prefix Prefix for the second, or right, input. Use the specified prefix when defining the right input in the On join condition. The processor adds the prefix to columns from the right input when identical column names exist in the left input.
Default is
t2_.Available with the On join command.
Join Using Columns Columns to use with the Using join condition. You can enter column names or select columns from preview data. Available with the Using join command.
Columns to Join On Names of the columns with values used to perform the join. Specify a column name for the Input 1 (Left) and the Input 2 (Right) properties. You can enter column names or select columns from preview data. Columns can have identical or unique names.
Click Add Another to specify another set of join columns.
Not available for Cross joins.