Aggregate
For example, you can use the Aggregate processor to calculate the sum of all
purchases in a batch grouped by state, and to write the results to a
State_Total output column in each row.
When you configure the Aggregate processor to perform a calculation, you specify the aggregation column, aggregate function, and output column to use. You can specify multiple sets of calculations to perform. You can optionally specify columns to group by for the calculations.
Processing and Generated Rows
The Aggregate processor can perform one or more aggregate calculations on data in a batch. For each calculation that you want to perform, you specify the aggregate function, the column to use for the calculation, and an output column for the results.
By default, the processor performs calculations using all of the incoming data. To perform calculations on subsets of data, specify one or more columns to group by.
Rows generated by the Aggregate processor include the output columns and any specified group-by columns. All other columns from the incoming row are dropped.
Example
- Use the
COUNTfunction and output the results to aStateCountcolumn. - Use the
SUMfunction with theTotalcolumn, and output the results to aStateTotalcolumn. - Set the processor to group by the
Statecolumn.
Let's say a batch contains the following data:
| TransactionID | StoreID | State | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0032355 | 35 | MD | 230.40 |
| 0016433 | 20 | IL | 90.50 |
| 0016434 | 20 | IL | 489.23 |
| 0032356 | 35 | MD | 63.50 |
| 0032357 | 35 | MD | 150.49 |
StateCount and
StateTotal columns in each row as follows:| State | StateCount | StateTotal |
|---|---|---|
| MD | 3 | 444.39 |
| IL | 2 | 579.73 |
Joining Aggregate Data
Rows generated by the Aggregate processor include the output columns and any specified group-by columns. All other columns from the incoming row are dropped.
If you want to perform aggregate calculations, but do not want to discard the rest of the data, you can perform the aggregate calculations in a separate branch in the pipeline, and then merge the results back into the data.
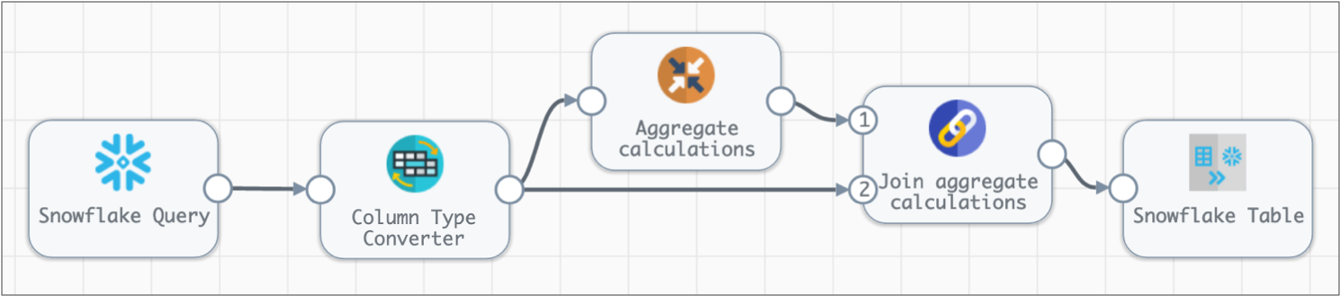
For example, the following pipeline converts a few column data types before passing the data to the Aggregate processor. Then, the Join processor joins the aggregate calculations with the data from the Column Type Converter processor.
Aggregate Functions
You can use the following aggregate functions in an Aggregate processor:
- Average - Returns the average of the values in a group.
- Count - Returns the number of items in a group.
- Count Distinct - Returns the number of unique items in a group.
- Max - Returns the maximum value of a group.
- Median - Returns the median of the values of a group.
- Min - Returns the minimum value of a group.
- Mode - Returns the most frequent value within a group.
- Standard Deviation - Returns the standard deviation of a value from the group. Standard deviation uses a sample of a group rather than the full population.
- Sum - Returns the sum of the values of a group.
- Variance - Returns a sample variance of non-NULL rows in a group.
- Custom - Returns the results of a custom aggregate calculation.
Configuring an Aggregate Processor
-
On the General tab, configure the following
properties:
General Property Description Name Stage name. Description Optional description. Cache Data Caches processed data. -
On the Aggregate tab, configure the following
properties:
Aggregate Property Description Aggregations The aggregate calculations to perform. Configure the following properties: - Aggregate Function - The aggregation
function to use in the calculation.
Default is Average.
- Aggregate Column - The column to use in the
aggregate calculation. You can enter the column name or select a column from preview
data.
Not available for all aggregate functions.
- Calculation - Aggregate calculation to use. Available when using Custom Calculation as the aggregate function.
- Output Column - The column for the results of the calculation.
Click the Add icon to add additional calculations.
Group By Columns Optional columns to group by. Use to perform calculations on subsets of the data. You can enter column names or select columns from preview data.
When you list more than one column, the processor uses the specified column order. If you specify multiple columns, you can drag them into the appropriate order.
When not used, the processor performs calculations across all rows in the batch.
- Aggregate Function - The aggregation
function to use in the calculation.