GCE Deployments
Applies to: IBM StreamSets as a Service
You can create a Google Compute Engine (GCE) deployment for an active GCP environment.
When you create a GCE deployment, you define the engine type, version, and configuration to deploy to the Google Cloud project and VPC network specified in the environment. You also specify the number of engine instances to deploy. Each engine instance runs on a dedicated Google Compute Engine VM instance.
When you start a GCE deployment, Control Hub connects to the project and VPC network specified in the environment and then uses Google Cloud Deployment Manager to create a Google deployment. Google Cloud Deployment Manager provisions the group of VM instances in the VPC network and then deploys and launches one IBM StreamSets engine instance on each VM instance.
Google Cloud Deployment Manager manages the provisioning and monitoring of the VM instances. Control Hub simply receives the status of the deployed engine instances and sends any updates to Deployment Manager.
When you stop a GCE deployment, Deployment Manager deletes the existing VM instances.
For more information about Google Cloud Deployment Manager, see the Google Cloud Deployment Manager documentation.
Before you create a GCE deployment, you must complete several prerequisites.
VM Instance Details
| Engine Type | Software |
|---|---|
| Data Collector 5.11.x and later |
|
| Data Collector 5.10.x and earlier |
|
| Transformer 6.0.x and later |
|
| Transformer 5.9.x |
|
| Transformer 5.8.x and earlier |
|
Secrets Policy
- Authentication token that the deployment uses to communicate with IBM StreamSets.
- Proxy credentials, including the HTTP and HTTPS proxy user and password, when you configure engines to use a proxy server.
- Automatic
- A secret with an automatic replication policy has its payload data replicated without restriction. This configuration is recommended for most users.
- User Managed
- A secret with a user managed replication policy has its payload data replicated to a set of locations that you specify. The secret can be replicated to one or more supported locations.
Prerequisites
- Create a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) environment
- Create and activate a GCP environment in Control Hub, as described in GCP Environments.
- Create an instance service account
- Ask your Google Cloud administrator to create an instance service account in Google Cloud to associate with the provisioned VM instances. If a default instance service account is defined for the parent GCP environment, you can skip this prerequisite and simply use the default. If a default is not set or if you'd like to override the default for the deployment, see Create Instance Service Accounts for VM Instances.
- Optionally, create an SSH key pair
- Control Hub does not use or require an SSH key pair to access the VM instances. However, if you’d like to use an SSH key to access the provisioned VM instances, create an SSH key pair to associate with the VM instances.
- Optionally, set up an external resource archive
- When your pipelines require external resources and when you plan to deploy multiple engine instances, you must set up an external resource archive that all engine instances can access. When your pipelines do not require external resources or when using a single engine instance to get started with IBM StreamSets, you do not need to complete this prerequisite.
Configuring a GCE Deployment
To create a new deployment, click in the Navigation panel, and then click the Create
Deployment icon: ![]() .
.
To edit an existing deployment, click in the Navigation panel, click the deployment name, and then click Edit.
Define the Deployment
Define the deployment essentials, including the deployment name and type, the environment that the deployment belongs to, and the engine type and version to deploy.
Once saved, you cannot change the deployment type, the engine version, or the environment.
-
Configure the following properties:
Define Deployment Property Description Deployment Name Name of the deployment. Use a brief name that informs your team of the deployment use case.
Deployment Type Select Google Compute Engine (GCE). Environment Active GCP environment where engine instances will be deployed. Engine Type Type of engine to deploy: - Data Collector
- Transformer
Engine Version Engine version to deploy. Deployment Tags Optional tags that identify similar deployments within Control Hub. Use deployment tags to easily search and filter deployments. Enter nested tags using the following format:
<tag1>/<tag2>/<tag3> -
If creating the deployment, click one of the following buttons:
- Cancel - Cancels creating the deployment and exits the wizard.
- Save & Next - Saves the deployment and continues.
- Save & Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the incomplete deployment in the Deployments view.
Configure the Engine
Define the configuration of the engine to deploy. You can use the defaults to get started.
-
Configure the following properties:
Engine Property Description Stage Libraries Stage libraries to install on the engine.
The available stage libraries depend on the selected engine type and version.
Advanced Configuration Access to advanced configuration properties to further customize the engine. As you get started with StreamSets, the default values should work in most cases.
The available properties depend on the selected engine type.
External Resource Source Source of the external files and libraries, such as JDBC drivers, required by the engine: - None - External resources are not defined in the
deployment.
Select when using a single engine instance to get started with IBM StreamSets, or when your pipelines do not require external resources.
- Archive File - External resources are included in an
archive file defined in the deployment.
Select when the deployment launches multiple engine instances and when your pipelines require external resources.
External Resource Location Location of the archive file that contains the external resources used by the engine. The archive file must be in TGZ or ZIP format.
Enter the location using one of the following formats:
- File path. For example: /mnt/shared/externalResources.tgz
- URL. For example, enter the URL as follows,
based on whether the file is stored in a private or
public Google Cloud Storage bucket:
- Private URL -
gs://<bucket_name>/<path>/externalResources.tgz - Public URL -
https://storage.googleapis.com/<bucket_name>/externalResources.tgz
- Private URL -
Tip: Click the download icon to download a sample externalResources.tgz file to view the required directory structure.Available when using an archive file as the source for external resources.
Engine Labels Labels to assign to all engine instances launched for this deployment. Labels determine the group of engine instances that run a job. Default is the name of the deployment.
Max CPU Load (%) Maximum percentage of CPU on the host machine that an engine instance can use. When an engine equals or exceeds this threshold, Control Hub does not start new pipeline instances on the engine.
All engine instances belonging to the deployment inherit these resource threshold values.
Default is 80.
Max Memory (%) Maximum percentage of the configured Java heap size that an engine instance can use. When an engine equals or exceeds this threshold, Control Hub does not start new pipeline instances on the engine.
Default is 100.
Max Running Pipeline Count Maximum number of pipelines that can be running on each engine instance. When an engine equals this threshold, Control Hub does not start new pipeline instances on the engine.
Default is 1,000,000.
- None - External resources are not defined in the
deployment.
-
If creating the deployment, click one of the following buttons:
- Back - Returns to the previous step in the wizard.
- Save & Next - Saves the deployment and continues.
- Save & Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the incomplete deployment in the Deployments view.
Configure the GCE Region and Secrets Policy
Select the region to provision the Google Compute Engine VM instances in and the replication policy type for GCP Secret Manager secrets.
-
Configure the following properties:
GCE Property Description Region GCE region to provision the VM instances in. Secret Replication Policy Replication policy type for the deployment information stored as GCP Secret Manager secrets: - Automatic - Secret payload data is replicated without restriction.
- User Managed - Secret payload data is replicated to a set of locations that you specify. Required when your Google Cloud organization has disabled global resource creation.
Default is Automatic.
Secret Locations One or more locations to replicate the secrets to. Note: When you specify multiple locations, a user managed replication policy costs more than an automatic policy because Google Cloud billing considers each location as a separate location.Available when using the user managed replication policy.
-
If creating the deployment, click one of the following buttons:
- Back - Returns to the previous step in the wizard.
- Save & Next - Saves the deployment and continues.
- Save & Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the incomplete deployment in the Deployments view.
Configure the GCE Zone and Subnet
Select one or more zones and a subnet to provision the Google Compute Engine VM instances in. You can select from the available zones and subnets within the selected GCE region and VPC network.
-
Configure the following properties:
GCE Property Description Zone One or more zones to provision the VM instances in. Subnet Subnet to provision the VM instances in. -
If creating the deployment, click one of the following buttons:
- Back - Returns to the previous step in the wizard.
- Save & Next - Saves the deployment and continues.
- Save & Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the incomplete deployment in the Deployments view.
Configure the GCE Autoscaling Group
Configure details about the Google Compute Engine VM instances that will be provisioned.
-
Configure the following properties:
GCE Autoscaling Group Property Description Desired Instances Number of engine instances to deploy. For each instance, Google Cloud Deployment Manager provisions a VM instance in the VPC, and then deploys and launches one engine instance on each VM instance.Important: If your pipelines require external resources, you must set up an external resource archive that all engine instances can access before increasing the number of instances.Default is 1. Set to the minimum value of 0 to temporarily prevent engine instances from running, as an alternative to stopping the deployment but that still incurs minimal costs from the cloud service provider.
Machine Type Machine type to use for the provisioned VM instances. For more information about the types, see the Google Cloud Compute Engine documentation.
Instance Service Account Instance service account to associate with the provisioned VM instances. Select the instance service account created as an environment prerequisite by your Google Cloud administrator. If a default instance service account is defined for the GCP environment, the default account is selected. You can accept the default or override it with a different instance service account.
GCP Labels Labels to apply to all Google Cloud resources provisioned for this deployment. Enter the labels as key-value pairs. For label naming requirements, see the Google Cloud Compute Engine documentation.
You can define the labels using simple or bulk edit mode. In simple edit mode, click Add to define additional labels. In bulk edit mode, configure labels in JSON format.
Important: These labels are applied to Google Cloud resources, not to Control Hub deployments.Network Tags Optional network tags that determine the firewall rules to apply to the provisioned VM instances. Enter the names of one or more network tags. When not specified, the firewall rules defined for the Google VPC network are applied to the provisioned VM instances.
The firewall rules must meet the requirements as described in Firewall Rules.
Init Script Initialization script to run on each provisioned instance.
Use the script to set up provisioned instances with additional software as required by your organization. The script must be a valid shell script with a maximum size of 8 KB.
Enter the script directly in the property or upload a shell script file that uses an
.shextension. After uploading, you can edit the contents of the script. -
If creating the deployment, click one of the following buttons:
- Back - Returns to the previous step in the wizard.
- Save & Next - Saves the deployment and continues.
- Save & Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the incomplete deployment in the Deployments view.
Configure GCE SSH Access
Optionally, configure SSH key access for the provisioned Google Compute Engine VM instances and whether to attach external IP addresses to the instances.
-
Configure the following properties:
GCE SSH Access Property Description Public SSH Key Full contents of the public SSH key to associate with each provisioned VM instance. Associating an SSH key with the instances is optional. If you choose to use an SSH key, enter the key created as a deployment prerequisite by your Google Cloud administrator.
Block Project-Wide SSH Keys Block the use of project-wide public SSH keys to access the provisioned VM instances. Attach Public IP Attach a public IP address to the provisioned VM instances. Enabled by default. In most cases, use the default because IBM StreamSets engines must create outbound connections to the internet.
Clear only when your GCP project does not allow externally accessible IP addresses and your Google Cloud administrator has created a Google Cloud NAT gateway as an environment prerequisite.
-
If creating the deployment, click one of the following buttons:
- Back - Returns to the previous step in the wizard.
- Save & Next - Saves the deployment and continues.
- Save & Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the incomplete deployment in the Deployments view.
Share the Deployment
By default, the deployment can only be seen by you. Share the deployment with other users and groups to grant them access to it.
- In the Select Users and Groups field, type a user email address or a group name.
-
Select users or groups from the list, and then click
Add.
The added users and groups display in the User / Group table.
-
Modify permissions as needed. By default, each added user
or group is granted the following permissions:
- Read - View the details of the deployment and of all engines managed by the deployment. Restart or shut down individual engines managed by the deployment in the Engines view.
- Write - Edit, start, stop, and delete the deployment. Delete engines managed by the deployment. Also requires read access on the parent environment.
- Execute - Start jobs on engines managed by the deployment. Starting jobs also requires execute access on the job and read access on the pipeline.
For more information, see Deployment Permissions.
-
Click one of the following buttons:
- Back - Returns to the previous step in the wizard.
- Save & Next - Saves the deployment and continues.
- Save & Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the incomplete deployment in the Deployments view.
Review and Launch the Deployment
You've successfully finished creating the deployment.
-
Click one of the following buttons:
- Exit - Saves the deployment and exits the wizard, displaying the Deactivated deployment in the Deployments view. You can start the deployment at a later time.
- Launch Deployment - Starts the deployment, provisions Google Compute Engine VM instances in your Google VPC network, and launches an IBM StreamSets engine on each instance.
-
If the deployment launches a Transformer engine that works with a Spark cluster, you must grant the Spark cluster
access to Transformer.
For instructions, see Granting the Spark Cluster Access to Transformer in the Transformer engine documentation.
Editing a GCE Deployment
You can edit a GCE deployment while it is deactivated or active.
When you stop a deployment, all existing VM instances are deleted. After you edit properties and then restart the deployment, Control Hub uses Google Cloud Deployment Manager to provision a new group of VM instances and launch a new IBM StreamSets engine instance on each VM instance.
- General deployment or engine properties
- When you edit general deployment or engine properties while the deployment is active, Google Cloud Deployment Manager continues running the existing VM instances. Changes to all engine instances are replicated on the next restart of the engines.
- GCE properties
- When you edit GCE properties while the deployment is active, Google Cloud Deployment Manager replaces all of the existing VM instances. This results in engine downtime while the new instances are being provisioned.
To edit a deployment, locate the deployment in the Deployments
view. In the Actions column, click the
More icon (![]() ) and then click Edit.
) and then click Edit.
Tracking URL
When you view the details of an active GCE deployment, you can access a tracking URL to the Google Cloud Console. Use the URL to view details about the Google Cloud resources automatically provisioned for the IBM StreamSets deployment.
To access the tracking URL, click a GCE deployment name in the Deployments view and then locate the Tracking URL property in the deployment details.
- VM instance template
- Managed instance group
- Autoscaler
For example, the following image displays a sample overview page:
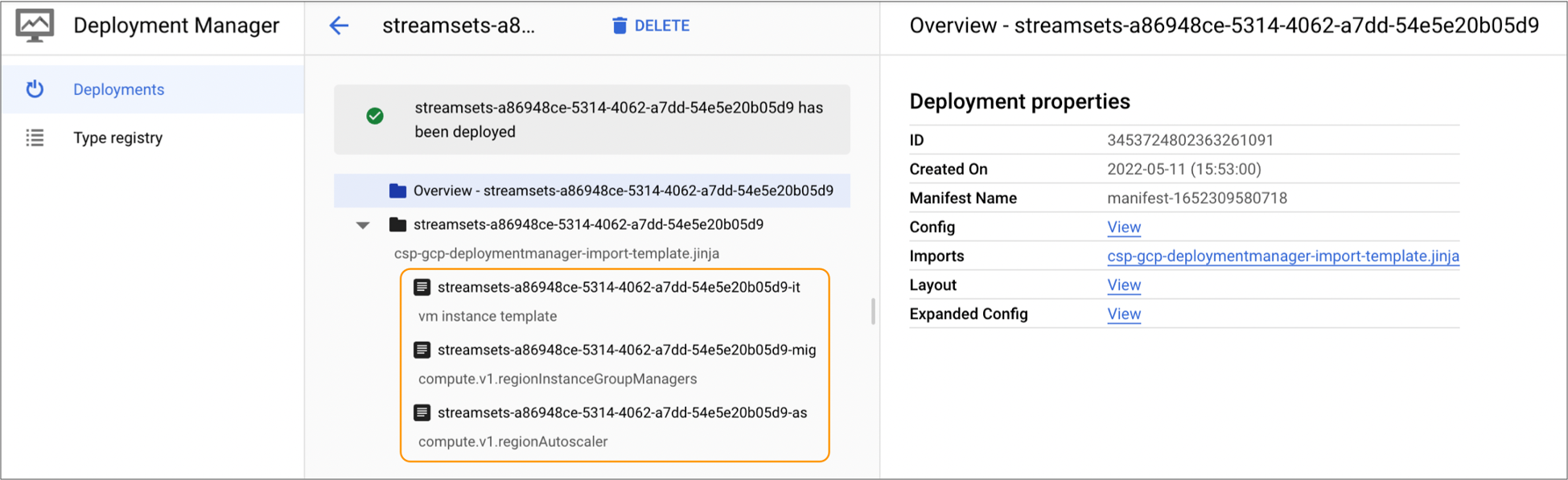
The following topics provide brief tips on finding the most useful information about the provisioned resources. For more details about monitoring a Google Cloud deployment, see the Google Cloud documentation.
VM Instance Template
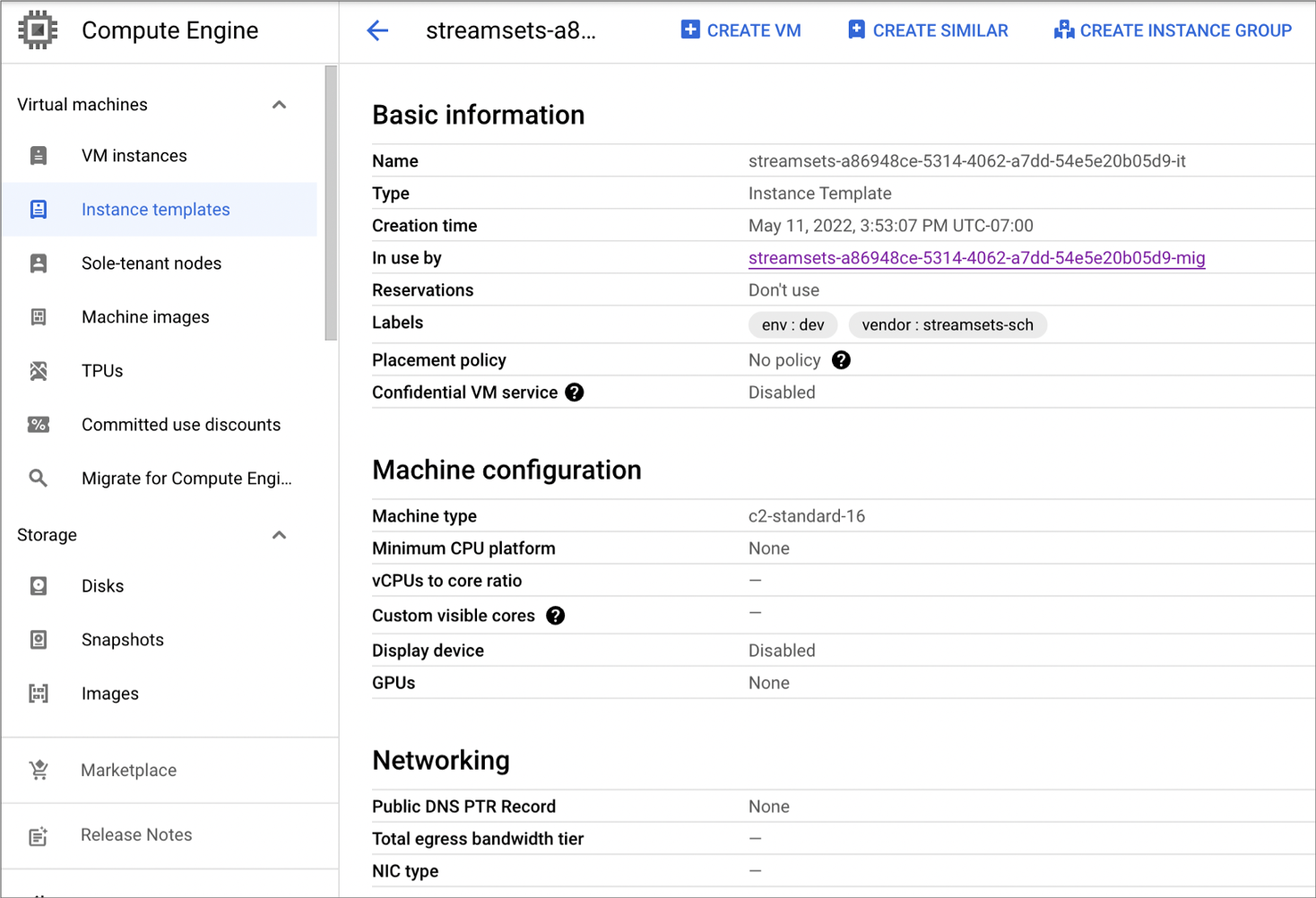
In the Google deployment overview page, click the link to the VM instance template and then click Manage Resource on the right.
The Google Cloud Console displays the following details about the instance template. Use the details to verify that the IBM StreamSets parent environment and deployment are configured with the correct values, such as the networking information or the SSH key:
Managed Instance Group
In the Google deployment overview page, click the link to the managed instance group and then click Manage Resource on the right.
The Google Cloud Console displays details about the instance group, including the status of the instance group, the number of provisioned VM instances, and an Errors tab. The Errors tab lists errors that occurred while provisioning the managed instance group; however, the list is not necessarily comprehensive.
For example, the following image displays an instance group with a Ready status that includes one VM instance:
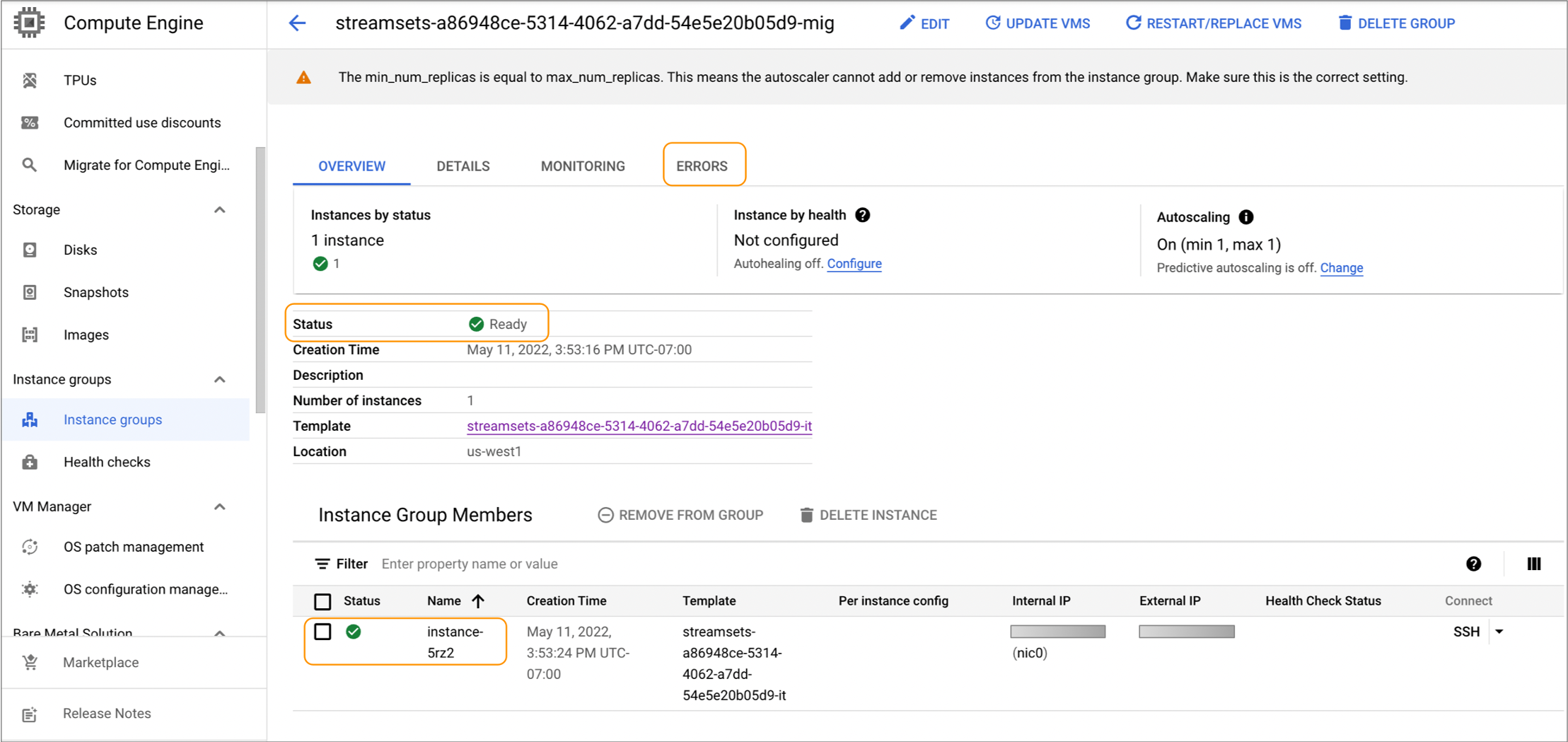
In the Instance Group Members section, click an instance name to view specific details about the VM instance. For example, click instance-5rz2 in the image above. The VM instance details page also allows you to use SSH to connect to the VM instance, even if you didn't provide an SSH key when creating the deployment.