Salesforce Lookup
The Salesforce Lookup processor performs lookups in a Salesforce object and passes the lookup values to fields. The processor can perform lookups with the SOAP or Bulk API. To perform lookups using Salesforce Bulk API 2.0, use the Salesforce Bulk API 2.0 Lookup processor. For information about supported versions, see Supported Systems and Versions.
Use the Salesforce Lookup processor to enrich records with additional data. For example,
you can configure the processor to use an account_number field as the
field to look up account name values in a Salesforce object, and pass the values to a
new account_name output field.
When a lookup results in multiple matches, the Salesforce Lookup processor can return the first matching value or return all matching values in separate records.
When you configure the Salesforce Lookup processor, you define connection information that the processor uses to connect to Salesforce, including the Salesforce API version and the authentication to use. You can also use a connection to configure the processor.
You specify the lookup mode and related properties, the output fields for returned values, and the multiple match behavior. You can optionally define a default value to use for fields with missing values and set the behavior for fields with missing values and no default value. You can also configure the processor to locally cache the lookup values to improve performance.
When using the SOQL Query lookup mode, and either the SOAP API or the Bulk API version 39.0 or later, you can configure the processor to retrieve deleted records from the Salesforce recycle bin.
You can optionally use an HTTP proxy to connect to Salesforce. When enabled in Salesforce, you can also configure the processor to use mutual authentication.
The processor generates Salesforce field attributes that provide additional information about each field.
Lookup Mode
The Salesforce Lookup processor can use two modes to look up Salesforce data. Select one of the following modes:
- Retrieve
- In Retrieve mode, the Salesforce Lookup processor uses the specified
Idfield to perform the lookup, making a single retrieve() Salesforce API call for up to 2000 records at a time. If one or more of the IDs included in an API call is invalid, Salesforce rejects the entire set of records. Then, the Salesforce Lookup processor sends the records to error, using the configured error handling for the stage. - SOQL Query
- In SOQL Query mode, the Salesforce Lookup processor makes an API call for each record. The processor uses a query() API call by default, and uses a queryAll() API call when including deleted records in the results.
Aggregate Functions in SOQL Queries
In SOQL Query mode, you can include SOQL
aggregate functions in the SELECT statements of SOQL queries. With one exception, the
processor places the result from the first function of a query into the
expr0 field, the result from the second function of the same query
into the expr1 field, and so on. The exception is the COUNT function
used without a field name - the processor always places that result into the
count field. The resulting field types depend on the functions and
queried fields. The stage does not generate field header attributes for the fields
resulting from aggregate functions. You can only include both aggregate functions and
non-aggregated fields in the same SELECT statement when you group by the non-aggregated
fields.
The following examples demonstrate some uses of aggregate functions in SOQL queries. Each
example examines data in the Account object where the name begins with the value in the
prefix field of the current record.
COUNT Function
Suppose you want the count of matching Salesforce records.
-
Without a field name, enter the following query:
SELECT COUNT() FROM Account WHERE Name LIKE '${record:value('/prefix')}%'When the COUNT function specifies no field name, the SELECT statement can contain no other elements.
In this case, the stage places the result from the function into the
countInteger field. -
With a field name, enter the following query:
SELECT COUNT(Id) FROM Account WHERE Name LIKE '${record:value('/prefix')}%'When the COUNT function includes a field name, the SELECT statement can include other aggregate functions.
In this case, the stage places the result from the function into the
expr0Integer field.
For more information about using the COUNT function with or without a field name, see the Salesforce developer documentation.
Multiple Aggregate Functions
You can use multiple aggregate functions in a single query.
Suppose that for the matching Salesforce records, you want the count, the most recent date that a record changed, and the smallest number of employees in any record.
SELECT COUNT(Id), MAX(LastModifiedDate), MIN(NumberOfEmployees) FROM Account
WHERE Name LIKE '${record:value('/prefix')}%'expr0- Integer field contains count of recordsexpr1- Datetime field contains last modified date-
expr2- Integer field contains number of employees
GROUP BY Clause
You can combine aggregate functions with a GROUP BY clause to compute values for groups of Salesforce records.
Suppose that for the matching Salesforce records, you want the unique values in the
Industry field along with count of records, last modified date,
and minimum number of employees in each industry.
SELECT Industry, COUNT(Id), MAX(LastModifiedDate), MIN(NumberOfEmployees) FROM Account
WHERE Name LIKE '${record:value('/prefix')}%'
GROUP BY Industry
Industry- String fieldexpr0- Integer field contains countexpr1- Datetime field contains last modified dateexpr2- Integer field contains number of employees
Field Aliases
You can use field aliases in the query to specify the field names where the stage places function results.
Suppose you want the count of records placed into the cnt field, the
most recent date that a record was changed placed into the
max_modify field, and the minimum number of employees placed
into the min_employees field.
SELECT COUNT(Id) cnt, MAX(LastModifiedDate) max_modify, MIN(NumberOfEmployees) min_employees FROM Account
WHERE Name LIKE '${record:value('/prefix')}%'
cnt- Integer fieldmax_modify- Datetime fieldmin_employees- Integer field
You cannot specify a SOQL keyword, such as count, as an alias.
In the Salesforce Lookup processor, you can use field mappings on the Lookup tab
rather than using field aliases. In the Salesforce Field property, enter the default
field, such as expr0. In the SDC Field property, enter the
preferred field name to place the function results. When using field mappings, you
can use SOQL keywords, such as count. You can also convert data
types.
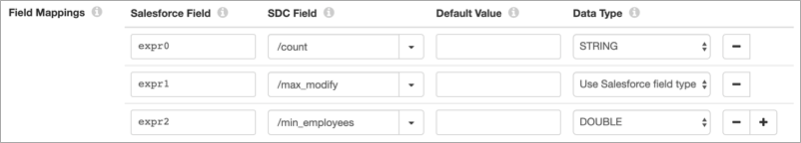
For example, to place the results from the query into the count
String field, max_modify Datetime field, and
min_employees Double field, configure the Field Mappings
property on the Lookup tab as follows:
Lookup Cache
To improve pipeline performance, you can configure the Salesforce Lookup processor to locally cache the values returned from a Salesforce object.
The processor caches values until the cache reaches the maximum size or the expiration time. When the first limit is reached, the processor evicts values from the cache.
- Size-based eviction
- Configure the maximum number of values that the processor caches. When the maximum number is reached, the processor evicts the oldest values from the cache.
- Time-based eviction
- Configure the amount of time that a value can remain in the cache without being written to or accessed. When the expiration time is reached, the processor evicts the value from the cache. The eviction policy determines whether the processor measures the expiration time since the last write of the value or since the last access of the value.
When you stop the pipeline, the processor clears the cache.
Salesforce Attributes
The Salesforce Lookup processor generates Salesforce field attributes that provide additional information about each field. The processor receives these details from Salesforce.
Salesforce attributes include a user-defined prefix to
differentiate the Salesforce attributes from other attributes. The prefix is
salesforce. by default. You can change the prefix that the
processor uses and you can configure the processor not to create Salesforce
attributes.
You can use the record:fieldAttribute or
record:fieldAttributeOrDefault functions to access the information
in the attribute.
The Salesforce Lookup processor can provide the following Salesforce field attributes:
| Salesforce Field Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| <Salesforce prefix>salesforceType | Provides the original Salesforce data type for the field. |
| <Salesforce prefix>length | Provides the original length for all string and textarea fields. |
| <Salesforce prefix>precision | Provides the original precision for all double fields. |
| <Salesforce prefix>scale | Provides the original scale for all double fields. |
| <Salesforce prefix>digits | Provides the maximum number of digits for all integer fields. |
For more information about field attributes, see Field Attributes.
Changing the API Version
Data Collector ships with version 57.0.0 of the Salesforce Web Services Connector libraries. You can use a different Salesforce API version if you need to access functionality not present in version 57.0.0.
- On the Salesforce tab, set the API Version property to the version that you want to use.
-
Download the relevant version of the following JAR files from Salesforce Web
Services Connector (WSC):
-
WSC JAR file - force-wsc-<version>.0.0.jar
-
Partner API JAR file - force-partner-api-<version>.0.0.jar
Where
<version>is the API version number.For information about downloading libraries from Salesforce WSC, see the Salesforce Developer documentation.
-
-
In the following Data Collector
directory, replace the default force-wsc-
57.0.0.jar and force-partner-api-57.0.0.jar files with the versioned JAR files that you downloaded:$SDC_DIST/streamsets-libs/streamsets-datacollector-salesforce-lib/lib/ - Restart Data Collector for the changes to take effect.
Configuring a Salesforce Lookup Processor
Configure a Salesforce Lookup processor to perform lookups in a Salesforce object. The processor can perform lookups using the SOAP or Bulk API.
-
In the Properties panel, on the General tab, configure the
following properties:
General Property Description Name Stage name. Description Optional description. Required Fields Fields that must include data for the record to be passed into the stage. Tip: You might include fields that the stage uses.Records that do not include all required fields are processed based on the error handling configured for the pipeline.
Preconditions Conditions that must evaluate to TRUE to allow a record to enter the stage for processing. Click Add to create additional preconditions. Records that do not meet all preconditions are processed based on the error handling configured for the stage.
On Record Error Error record handling for the stage: - Discard - Discards the record.
- Send to Error - Sends the record to the pipeline for error handling.
- Stop Pipeline - Stops the pipeline.
-
On the Salesforce tab, configure the following
properties:
Salesforce Property Description Connection Connection that defines the information required to connect to an external system. To connect to an external system, you can select a connection that contains the details, or you can directly enter the details in the pipeline. When you select a connection, Control Hub hides other properties so that you cannot directly enter connection details in the pipeline.
To create a new connection, click the Add New Connection icon:
 . To view and edit the details of the
selected connection, click the Edit
Connection icon:
. To view and edit the details of the
selected connection, click the Edit
Connection icon:  .
.Auth Endpoint Salesforce SOAP API authentication endpoint. For example, you might enter one of the following common values: login.salesforce.com- Use to connect to a Production or Developer Edition organization.test.salesforce.com- Use to connect to a sandbox organization.
Default is
login.salesforce.com.API Version Salesforce API version used to connect to Salesforce. Default is 57.0.0. If you change the version, you also must download the relevant JAR files from Salesforce Web Services Connector (WSC).
Authentication Type Authentication type to use to connect to Salesforce: - Basic Authentication - Specify a user name and password.
- Connected App with OAuth - Use an OAuth 2.0-enabled connected app to enable machine-to-machine OAuth with JWT Bearer Flow.
Username Salesforce username in the following email format: <text>@<text>.com.When using Connected App with OAuth authentication, the user must be authorized to use the app.
Password Salesforce password.
If the Data Collector machine is outside the trusted IP range configured in your Salesforce environment, you must use a security token along with the password. Use Salesforce to generate a security token and then set this property to the password followed by the security token.
For example, if the password is
abcdand the security token is1234, then set this property to abcd1234. For more information on generating a security token, see Reset Your Security Token.Tip: To secure sensitive information such as user names and passwords, you can use runtime resources or credential stores.Consumer Key Consumer key from the connected app. Tip: To secure sensitive information such as user names and passwords, you can use runtime resources or credential stores.Available when using Connected App with OAuth authentication.
Private Key Private key from the public key certificate that you used with the connected app. Ensure that the key is formatted correctly, with no spaces or extra line breaks. Tip: To secure sensitive information such as user names and passwords, you can use runtime resources or credential stores.Available when using Connected App with OAuth authentication.
Subscribe Timeout Maximum time to allow for subscribing to a Salesforce channel, in seconds. Connection Handshake Timeout Maximum time to wait for a Salesforce connection handshake, in seconds. -
On the Lookup tab, configure the following
properties:
Lookup Property Description Lookup Mode Lookup mode to use: - Retrieve - Use to perform a lookup for up to 2000 records at a time from the specified object, based on the specified Id field. Use when possible to improve pipeline performance.
- SOQL Query - Use to perform a record-by-record lookup based on a specified query. Can retrieve deleted records and access data in related objects.
Default is SOQL Query.
SOQL Query SOQL query to use to look up data in Salesforce. Use the following syntax for the query: SELECT <field1 name>, <field2 name> FROM <object name> WHERE <field3 name> <operator> <expression>For more information, see Lookup Mode.
For SOQL Query mode only.
Include Deleted Records Determines whether the SOQL query also retrieves deleted records from the Salesforce recycle bin. The query can retrieve deleted records when the stage uses the Salesforce SOAP API or the Bulk API version 39.0 or later. Earlier versions of the Bulk API do not support retrieving deleted records.
For SOQL Query mode only.
Id Field Field in the record containing the Salesforce record ID to use for the lookup. For Retrieve mode only.
Salesforce Fields A comma-separated list of Salesforce fields to return. For Retrieve mode only.
Object Type The object type to use for the lookup. The object type must be considered retrievable by Salesforce. For Retrieve mode only.
Field Mappings Use to override the default field mappings. By default, Salesforce fields are written to Data Collector fields of the same name. Enter the following:- Salesforce Field - Name of the Salesforce field that contains the lookup value. Enter a field name or enter an expression that defines the field name.
- SDC Field - Name of the field in the record that receives the lookup value. You can specify an existing field or a new field. If the field does not exist, Salesforce Lookup creates the field.
- Default Value - Optional default value to use when the query does not return a value for the field. If the query returns no value and this property is not defined, the processor handles the record based on the Missing Values Behavior property.
- Data Type - Data type to use for SDC Field. Required when you specify a default value. The processor uses the Salesforce data type by default.
Using simple or bulk edit mode, click the Add icon to create additional field mappings.
Multiple Values Behavior Action to take upon finding multiple matching values: - First value only - Returns the first value.
- Split into multiple records - Returns every matching value in a separate record.
Missing Values Behavior Action to take upon finding no return values in fields with no default value defined: - Send to error - Sends the record to error.
- Pass the record along the pipeline unchanged - Passes the record without a lookup return value.
Enable Local Caching Specifies whether to locally cache the returned values. Maximum Entries to Cache Maximum number of values to cache. When the maximum number is reached, the processor evicts the oldest values from the cache. Default is -1, which means unlimited.
Eviction Policy Type Policy used to evict values from the local cache when the expiration time has passed: - Expire After Last Access - Measures the expiration time since the value was last accessed by a read or a write.
- Expire After Last Write - Measures the expiration time since the value was created, or since the value was last replaced.
Expiration Time Amount of time that a value can remain in the local cache without being accessed or written to. Default is 1 second.
Time Unit Unit of time for the expiration time. Default is seconds.
-
On the Advanced tab, configure the following
properties:
Advanced Property Description Use Proxy Specifies whether to use an HTTP proxy to connect to Salesforce. Proxy Hostname Proxy host. Proxy Port Proxy port. Proxy Requires Credentials Specifies whether the proxy requires a user name and password. Proxy Realm Authentication realm for the proxy server. Proxy Username User name for proxy credentials. Proxy Password Password for proxy credentials. Tip: To secure sensitive information such as user names and passwords, you can use runtime resources or credential stores.Create Salesforce Attributes Adds Salesforce field attributes to fields. The origin creates Salesforce attributes by default. Salesforce Attribute Prefix Prefix for Salesforce attributes. Use Mutual Authentication When enabled in Salesforce, you can use SSL/TLS mutual authentication to connect to Salesforce.
Mutual authentication is not enabled in Salesforce by default. To enable mutual authentication, contact Salesforce.
Before enabling mutual authentication, you must store a mutual authentication certificate in the Data Collector resources directory. For more information, see Keystore and Truststore Configuration.
Use Remote Keystore Enables loading the contents of the keystore from a remote credential store or from values entered in the stage properties. Private Key Private key used in the remote keystore. Enter a credential function that returns the key or enter the contents of the key. Certificate Chain Each PEM certificate used in the remote keystore. Enter a credential function that returns the certificate or enter the contents of the certificate. Keystore File Path to the local keystore file. Enter an absolute path to the file or enter the following expression to define the file stored in the Data Collector resources directory:
${runtime:resourcesDirPath()}/keystore.jksBy default, no keystore is used.
Keystore Type Type of keystore to use. Use one of the following types: - Java Keystore File (JKS)
- PKCS #12 (p12 file)
Default is Java Keystore File (JKS).
Keystore Password Password to the keystore file. A password is optional, but recommended.
Tip: To secure sensitive information such as passwords, you can use runtime resources or credential stores.Keystore Key Algorithm Algorithm to manage the keystore.
Default is SunX509.