Azure VM Deployments
Section Contents
Azure VM Deployments#
You can create an Azure Virtual Machine (Azure VM) deployment for an active Azure environment.
When you create an Azure VM deployment, you define the engine type, version, and configuration to deploy to the Azure virtual network (VNet) specified in the environment. You also specify the number of engine instances to deploy. Each engine instance runs on a dedicated VM instance.
For more details, refer to the StreamSets Platform Documentation.
Creating a Deployment for Data Collector#
The SDK is designed to mirror the UI workflow. This section shows you how to create an Azure VM deployment for Data Collector in the UI and how to achieve the same using StreamSets Platform SDK for Python code step by step.
Define the Deployment#
In the UI, a deployment is defined as seen below:
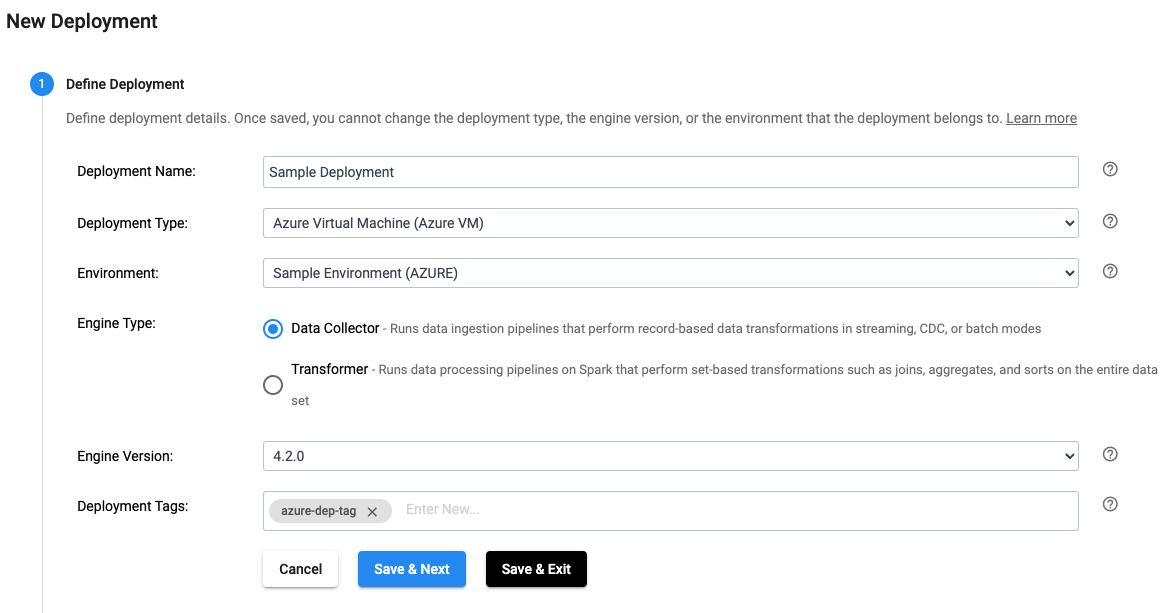
The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
deployment_builder = sch.get_deployment_builder(deployment_type='AZURE_VM')
# sample_environment is an instance of streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureEnvironment
deployment = deployment_builder.build(deployment_name='Sample Deployment',
environment=sample_environment,
engine_type='DC',
engine_version='4.2.0',
deployment_tags=['azure-dep-tag'])
Configure the Engine#
In the UI, a deployment’s engines are configured as seen below:
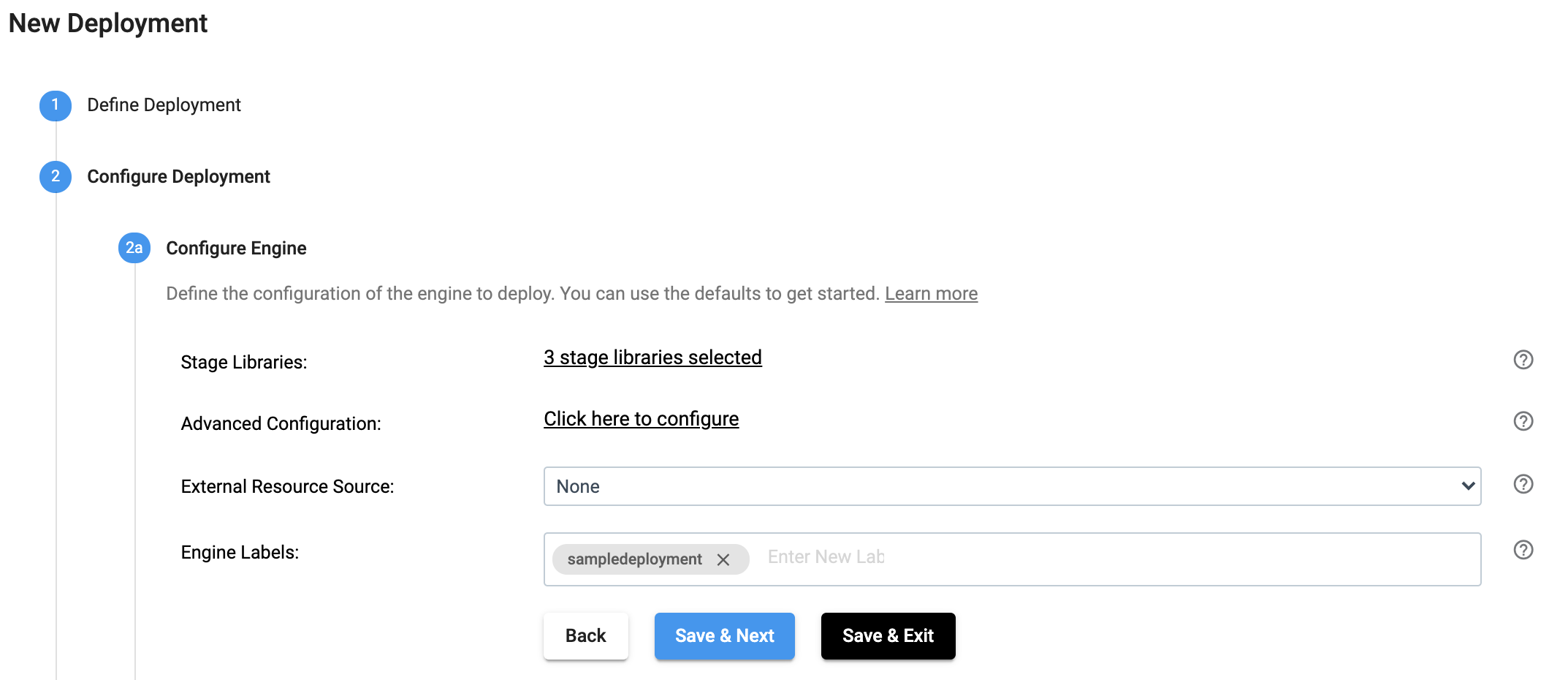
In the above UI, when you click on 3 stage libraries selected, the following dialog opens and allows you to select stage libraries.
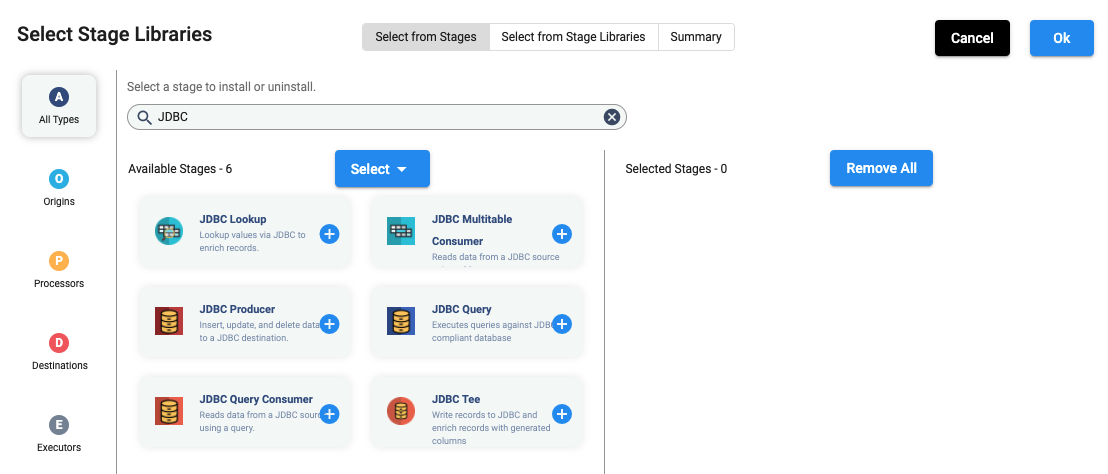
In the above UI, once you select JDBC and click on any of the ‘+’ signs, then it shows the following:
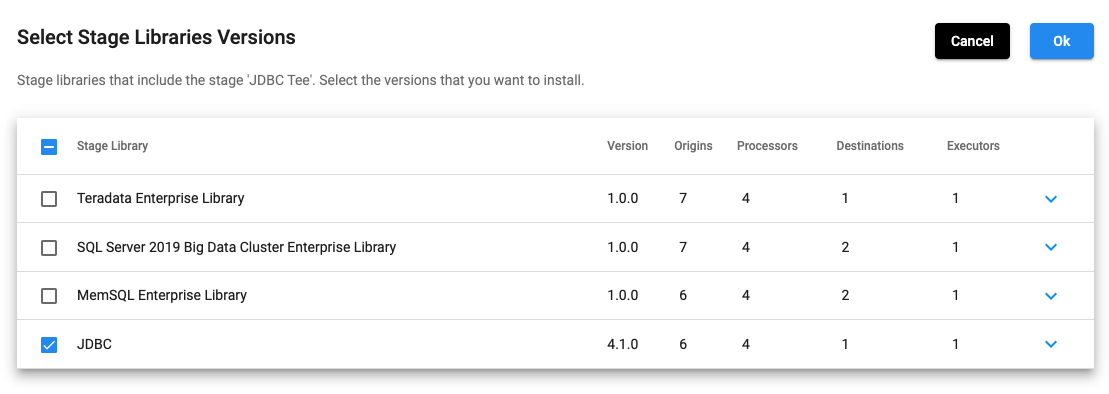
Selecting stage libraries for a deployment is also possible using the SDK. The stage_libs property of the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentEngineConfiguration attribute in a
Deployment object allows specification of additional stage libraries in the '<library_name>' format, or optionally
the '<library_name>:<library_version>' format.
Note
If a version is omitted for a stage library, it will default to the engine version that was configured for the deployment.
There are several methods available for modifying the stage libraries of a deployment.
If you know the complete list of stage libraries you want to add to a deployment, you can specify them as a list
and set the stage_libs attribute directly as seen below:
Warning
Attempting to add multiple versions of the same stage library to a deployment’s engine configuration will result in an error when you attempt to add or update a deployment on the StreamSets Platform.
# Stage libraries can be supplied both with and without version specified. Any without a version will default
# to the version of the engine selected for the deployment
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs = ['jdbc', 'aws:4.1.0', 'cdp_7_1:4.3.0', 'basic:4.3.0', 'dev']
The stage_libs attribute operates like a traditional list object, with accompanying append(),
extend(), and remove() methods.
If you are looking to add a single stage library to a deployment’s engine configuration, you can utilize the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentStageLibraries.append() method, using the same library:version syntax from
above:
# Adding a single additional library to the stage library configuration
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.append('aws')
If you would prefer to add a list of additional stage libraries to a deployment’s engine configuration, you can utilize
the streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentStageLibraries.extend() method, which also follows the same
library:version syntax from above:
# Extending the list of stage libraries by adding two additional stages
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.extend(['cassandra_3:4.3.0', 'elasticsearch_7'])
Finally, if you would like to remove a single stage library from a deployment’s engine configuration, you can utilize
the streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentStageLibraries.remove() method. The removal of a stage library from
a deployment’s engine configuration intentionally requires a version to be supplied, so as to not accidentally remove
an unintended stage library:
# Removing a single library from the stage library configuration by supplying the library name and version
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.remove('aws:4.1.0')
You can also configure an external resource as well as engine labels for the deployment:
# Optional - set external resource source and engine labels
deployment.engine_configuration.external_resource_source = <External resource source>
deployment.engine_configuration.engine_labels = ['sampledeployment']
Configure the Azure VM Autoscaling Group#
In the UI, the Azure VM Autoscaling Group for a deployment is configured as seen below:
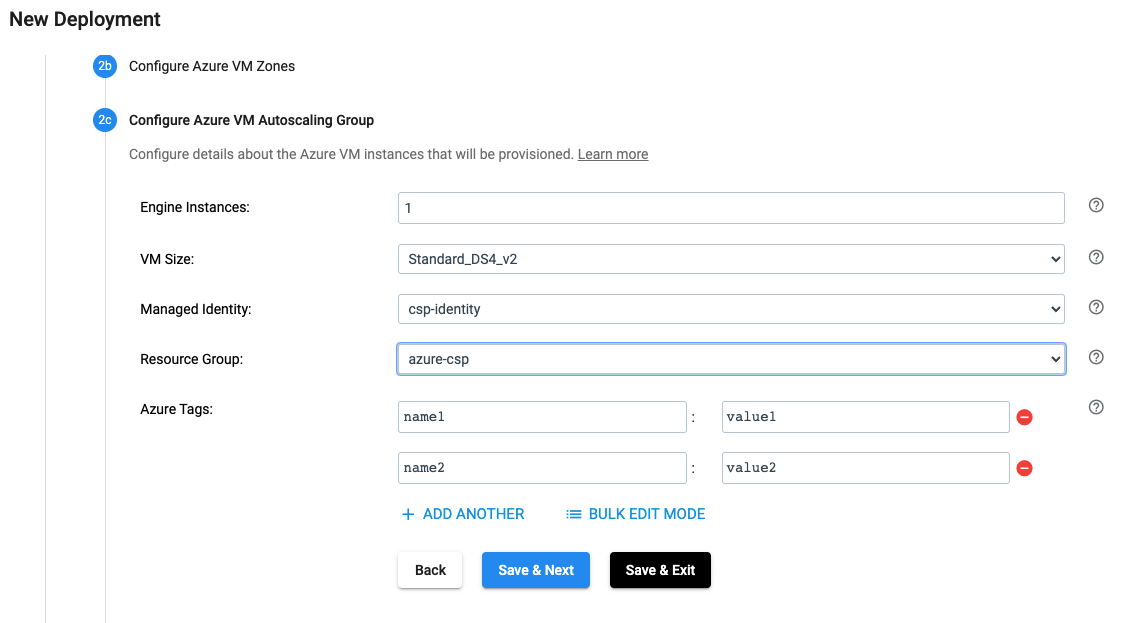
The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
deployment.engine_instances = 1
deployment.vm_size = 'Standard_D4s_v2'
deployment.managed_identity = 'csp-identity'
deployment.resource_group = 'azure-csp'
deployment.azure_tags = {'name1': 'value1', 'name2': 'value2'}
Configure Azure VM SSH Access#
In the UI, the Azure VM SSH Access for a deployment is configured as seen below:
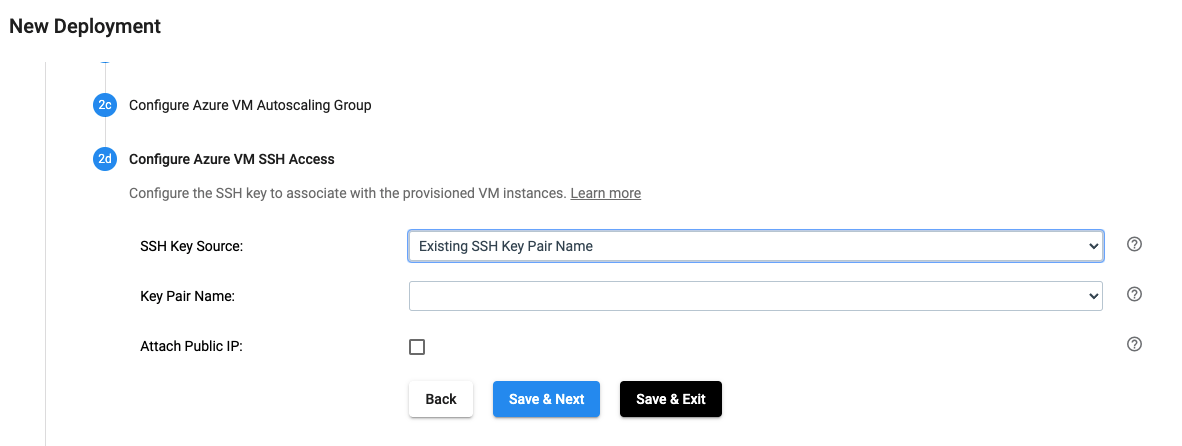
The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
deployment.ssh_key_source = 'Existing SSH Key Pair Name'
deployment.key_pair_name = <SSH key pair name>
deployment.attach_public_ip = False
Review and Launch the Deployment#
In the UI, a deployment can be reviewed and launched as seen below:

The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
sch.add_deployment(deployment)
# Optional - equivalent to clicking on 'Launch Deployment'
sch.start_deployment(deployment)
Complete example for Data Collector#
To create a new streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureVMDeployment object and add it to Control Hub, use the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentBuilder class.
Use the streamsets.sdk.ControlHub.get_deployment_builder() method to instantiate the builder object:
deployment_builder = sch.get_deployment_builder(deployment_type='AZURE_VM')
Next, retrieve the streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureEnvironment object which represents an active Azure
environment where engine instances will be deployed, pass it to the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentBuilder.build() method along with other parameters. Finally, pass the
resulting streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureVMDeployment object to the
streamsets.sdk.ControlHub.add_deployment() method:
# sample_environment is an instance of streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureEnvironment
deployment = deployment_builder.build(deployment_name='Sample Deployment',
environment=sample_environment,
engine_type='DC',
engine_version='4.2.0',
deployment_tags=['azure-dep-tag'])
# Optional - add sample stage libs
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs = ['jdbc', 'aws:4.1.0', 'cdp_7_1:4.3.0', 'basic:4.3.0', 'dev']
# deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.append('aws')
# deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.extend(['cassandra_3:4.3.0', 'elasticsearch_7'])
# Optional - set external resource source and engine labels
deployment.engine_configuration.external_resource_source = <External resource source>
deployment.engine_configuration.engine_labels = ['sampledeployment']
deployment.engine_instances = 1
deployment.vm_size = 'Standard_D4s_v2'
deployment.managed_identity = 'csp-identity'
deployment.resource_group = 'azure-csp'
deployment.azure_tags = {'name1': 'value1', 'name2': 'value2'}
deployment.ssh_key_source = 'Existing SSH Key Pair Name'
deployment.key_pair_name = <SSH key pair name>
deployment.attach_public_ip = False
sch.add_deployment(deployment)
# Optional - equivalent to clicking on 'Launch Deployment'
sch.start_deployment(deployment)
Creating a Deployment for Transformer#
The SDK is designed to mirror the UI workflow. This section shows you how to create an Azure VM deployment for Transformer in the UI and how to achieve the same using StreamSets Platform SDK for Python code step by step.
Define the Deployment#
In the UI, a deployment is defined as seen below:
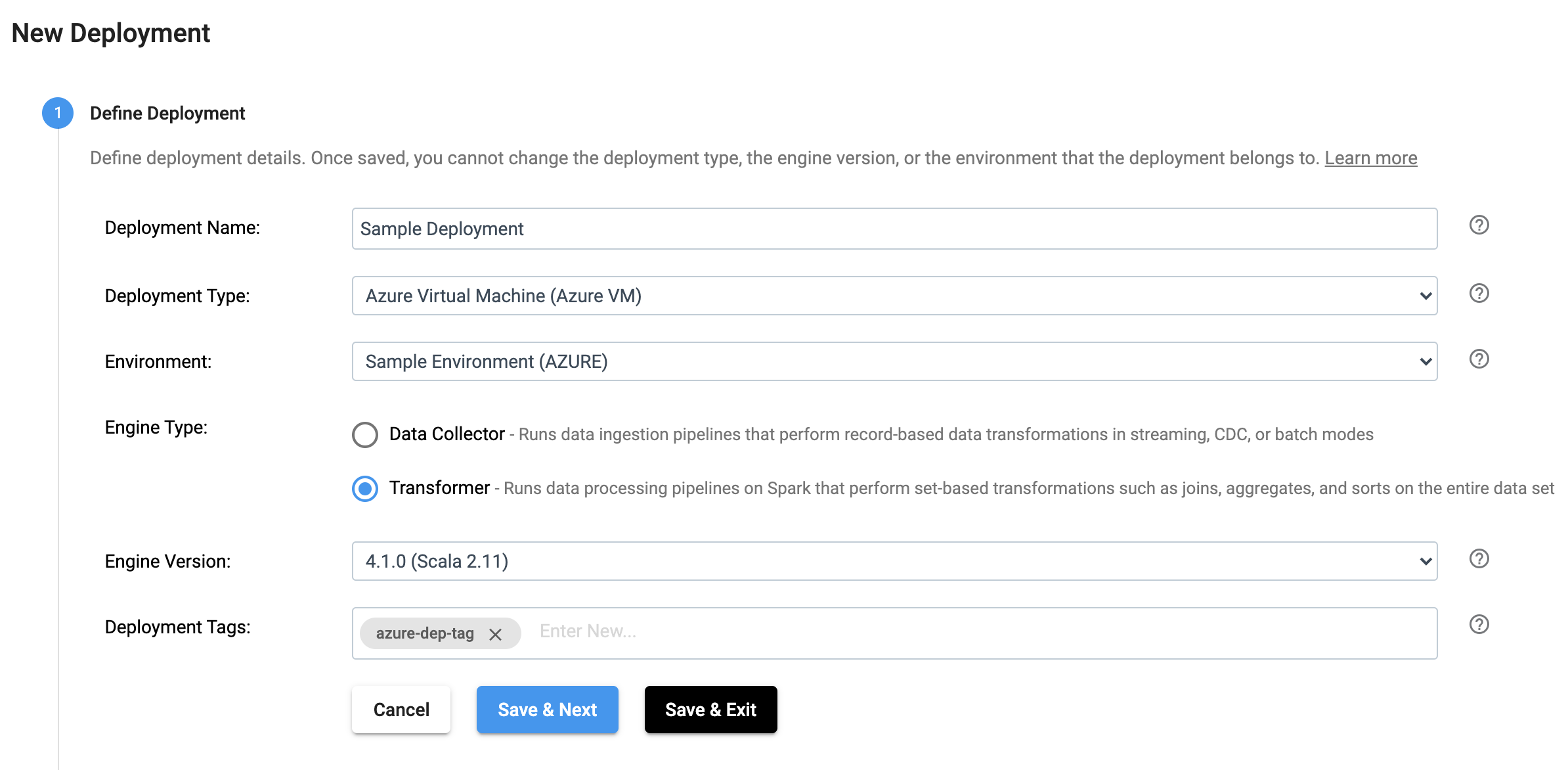
The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
deployment_builder = sch.get_deployment_builder(deployment_type='AZURE_VM')
# sample_environment is an instance of streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureEnvironment
deployment = deployment_builder.build(deployment_name='Sample Deployment',
environment=sample_environment,
engine_type='TF',
engine_version='4.1.0',
scala_binary_version='2.11.0',
deployment_tags=['azure-dep-tag'])
Configure the Engine#
In the UI, a deployment’s engines are configured as seen below:

In the above UI, when you click on 3 stage libraries selected, the following dialog opens and allows you to select stage libraries.
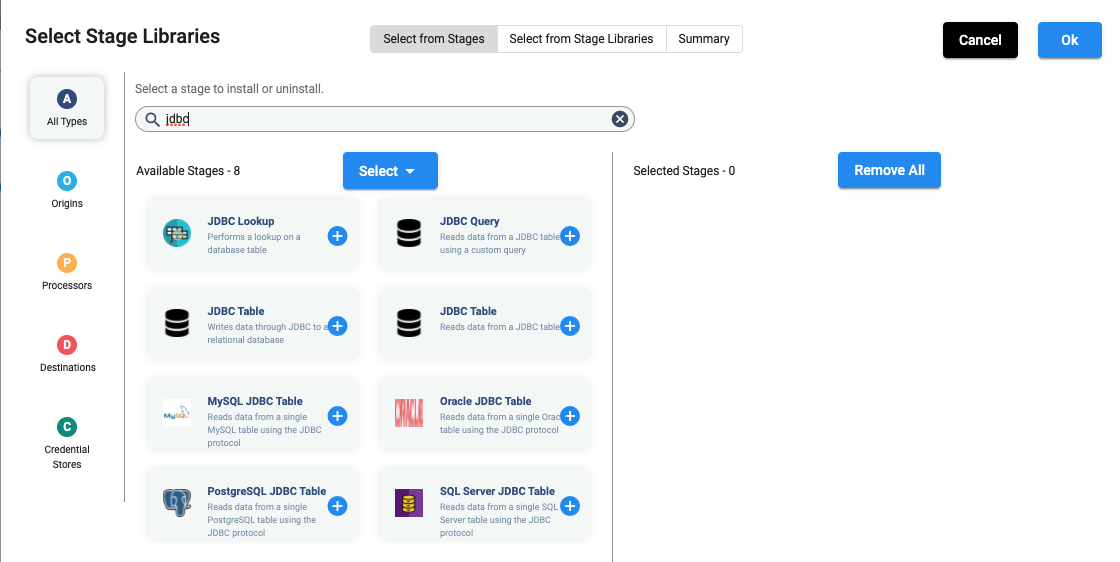
In the above UI, once you select JDBC and click on any of the ‘+’ signs, then it shows the following:
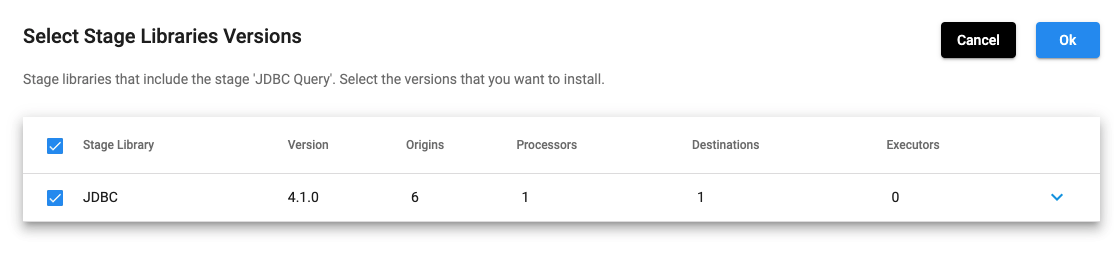
Selecting stage libraries for a deployment is also possible using the SDK. The stage_libs property of the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentEngineConfiguration attribute in a
Deployment object allows specification of additional stage libraries in the '<library_name>' format, or optionally
the '<library_name>:<library_version>' format.
Note
If a version is omitted for a stage library, it will default to the engine version that was configured for the deployment.
There are several methods available for modifying the stage libraries of a deployment.
If you know the complete list of stage libraries you want to add to a deployment, you can specify them as a list
and set the stage_libs attribute directly as seen below:
Warning
Attempting to add multiple versions of the same stage library to a deployment’s engine configuration will result in an error when you attempt to add or update a deployment on the StreamSets Platform.
# Stage libraries can be supplied both with and without version specified. Any without a version will default
# to the version of the engine selected for the deployment
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs = ['file', 'aws_3_2_0:4.2.0', 'jdbc', 'kafka:4.2.0']
The stage_libs attribute operates like a traditional list object, with accompanying append(),
extend(), and remove() methods.
If you are looking to add a single stage library to a deployment’s engine configuration, you can utilize the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentStageLibraries.append() method, using the same library:version syntax from
above:
# Adding a single additional library to the stage library configuration
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.append('hive:4.2.0')
If you wouldd prefer to add a list of additional stage libraries to a deployment’s engine configuration, you can utilize
the streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentStageLibraries.extend() method, which also follows the same
library:version syntax from above:
# Extending the list of stage libraries by adding two additional stages
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.extend(['redshift-no-dependency:4.2.0', 'azure_3_2_0'])
Finally, if you would like to remove a single stage library from a deployment’s engine configuration, you can utilize
the streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentStageLibraries.remove() method. The removal of a stage library from
a deployment’s engine configuration intentionally requires a version to be supplied, so as to not accidentally remove
an unintended stage library:
# Removing a single library from the stage library configuration by supplying the library name and version
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.remove('kafka:4.2.0')
You can also configure an external resource as well as engine labels for the deployment:
# Optional - set external resource source and engine labels
deployment.engine_configuration.external_resource_source = <External resource source>
deployment.engine_configuration.engine_labels = ['sampledeployment']
Configure the Azure VM Autoscaling Group#
In the UI, the Azure VM Autoscaling Group for a deployment is configured as seen below:

The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
deployment.engine_instances = 1
deployment.vm_size = 'Standard_D4s_v2'
deployment.managed_identity = 'csp-identity'
deployment.resource_group = 'azure-csp'
deployment.azure_tags = {'name1': 'value1', 'name2': 'value2'}
Configure Azure VM SSH Access#
In the UI, the Azure VM SSH Access for a deployment is configured as seen below:

The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
deployment.ssh_key_source = 'Existing SSH Key Pair Name'
deployment.key_pair_name = <SSH key pair name>
deployment.attach_public_ip = False
Review and Launch the Deployment#
In the UI, a deployment can be reviewed and launched as seen below:

The same effect can be achieved by using the SDK as seen below:
sch.add_deployment(deployment)
# Optional - equivalent to clicking on 'Launch Deployment'
sch.start_deployment(deployment)
Complete example for Transformer#
To create a new streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureVMDeployment object and add it to Control Hub, use the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentBuilder class.
Use the streamsets.sdk.ControlHub.get_deployment_builder() method to instantiate the builder object:
deployment_builder = sch.get_deployment_builder(deployment_type='AZURE_VM')
Next, retrieve the streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureEnvironment object which represents an active Azure
environment where engine instances will be deployed, pass it to the
streamsets.sdk.sch_models.DeploymentBuilder.build() method along with other parameters. Finally, pass the
resulting streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureVMDeployment object to the
streamsets.sdk.ControlHub.add_deployment() method:
# sample_environment is an instance of streamsets.sdk.sch_models.AzureEnvironment
deployment = deployment_builder.build(deployment_name='Sample Deployment',
environment=sample_environment,
engine_type='TF',
engine_version='4.1.0',
scala_binary_version='2.11.0',
deployment_tags=['azure-dep-tag'])
# Optional - add sample stage libs
deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs = ['file', 'aws_3_2_0:4.2.0', 'jdbc', 'kafka:4.2.0']
# deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.append('hive:4.2.0')
# deployment.engine_configuration.stage_libs.extend(['redshift-no-dependency:4.2.0', 'azure_3_2_0'])
# Optional - set external resource source
deployment.engine_configuration.external_resource_source = <External resource source>
deployment.engine_configuration.engine_labels = ['sampledeployment']
deployment.engine_instances = 1
deployment.vm_size = 'Standard_D4s_v2'
deployment.managed_identity = 'csp-identity'
deployment.resource_group = 'azure-csp'
deployment.azure_tags = {'name1': 'value1', 'name2': 'value2'}
deployment.ssh_key_source = 'Existing SSH Key Pair Name'
deployment.key_pair_name = <SSH key pair name>
deployment.attach_public_ip = False
sch.add_deployment(deployment)
# Optional - equivalent to clicking on 'Launch Deployment'
sch.start_deployment(deployment)