Expression Language
The IBM StreamSets expression language enables you to create expressions that evaluate or modify data. The IBM StreamSets expression language is based on the JSP 2.0 expression language.
Use the expression language to configure expressions and conditions in processors, such as the Expression Evaluator or Stream Selector. Some destination properties also allow the expression language, such as the directory template for the Hadoop FS destination.
You can use the expression language to define any stage or pipeline property that represents a numeric or string value. You can also use field path expressions to select the fields to use in some processors.
Use expression completion to determine where you can use an expression and the expression elements that you can use in that location.
- Constants
- Datetime variables
- Field names
- Functions
- Literals
- Operators
- Runtime parameters
- Runtime properties
- Runtime resources
For more information about using expressions in pipelines, see Expression Configuration.
Expression Completion in Properties
Expression completion provides a list of functions and other elements of the StreamSets expression language that are valid for use at that location. The list includes any runtime parameters that are defined for the pipeline, and available fields when the pipeline is valid for data preview.
When an element does not display in the list, it is not a valid element at the specified location.
Tips for Expression Completion
Use the following information and tips to work with expression completion:
- To invoke expression completion and see all available elements, place the cursor where
you want to create an expression and click Ctrl + Space Bar.
A list of valid expression elements displays. When an element does not display in the list, it is not a valid element at the specified location. Scroll to view the entire list.
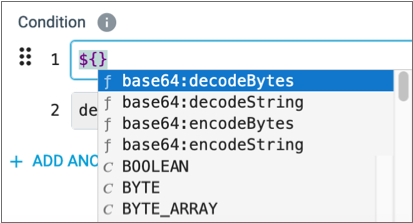
You can use expression completion wherever you can define an expression.
- You can filter the element list by typing a few letters of the element name.
Element names that include your input appear at the top of the list. Below that, it displays elements that include the individual letters that you entered.
- Expression completion automatically displays when possible when you type in an
expression.
For example, after typing in
rein an expression, the following list displays: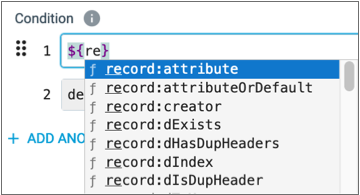
- Expression completion lists elements using the following icons:
cicon for constants-
ficon for functions - Square icon for fields
xicon for runtime parameters defined in the pipeline
In the following example,
RootDiris a runtime parameter: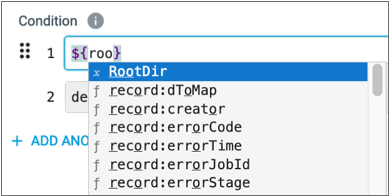
- To view more information about an element, highlight or select the element name:
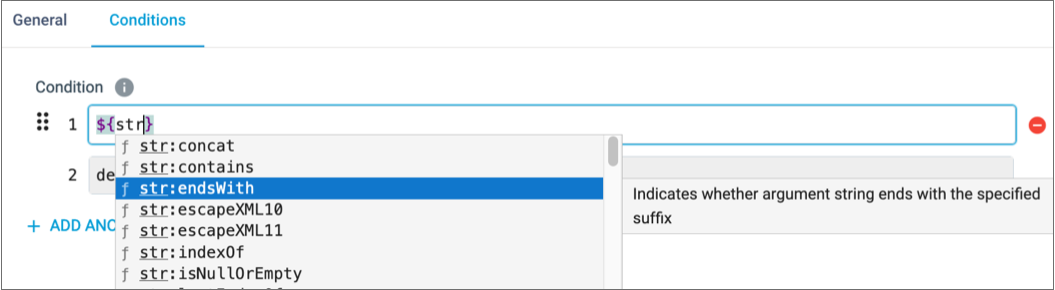
- To add an element to an expression, click the element name or use the Enter/Return key on the highlighted element.
- When you add a function, it displays with syntax placeholders. You can view the full
syntax by clicking within the parentheses.
Expression Examples
The following tables include some examples of how you might use expressions in the Data Collector.
- Conditions
- The following table includes some examples of conditions:
Sample Condition Expressions Description ${record:value('/payment_type') == 'CRD'} In a Stream Selector, this condition routes records where the payment type is credit card to the stream. ${record:value('[3]/State') == "MD"} The same as above, but for a record in list format. ${record:errorCode()=="FIELD_MERGER_02"} Used in a Stream Selector in an error pipeline, this condition routes records with the FIELD_MERGER_02 error to a stream that corrects the error. ${record:value("[20]/value") == ""} When used in an alert, triggers an alert when the specified field contains no data. ${record:type('/ID')=STRING} In the Stream Selector, routes records where the ID is a String to a branch that includes a Field Type Converter to convert the field to a numeric data type. - if-then-else
- The following table includes some examples of if-then-else
expressions:
Sample if-then-else Expressions Description ${record:value('/gender')=='1'?'M':(record:value('/gender')=='2'?'F':'U')}
Replaces 1 with "M", 2 with "F", and any other value with "U" for unknown. ${record:value('/phone_home') != ' ' ? record:value('/phone_home'):
(record:value('/phone_mobile') != ' ' ? record:value('/phone_mobile'):
(record:value('/phone_work') != ' ' ? record:value('/phone_work'): ' '))}
The phone number to use for a primary_phone field based on phone numbers in the home_phone, mobile_phone and work_phone fields:- If there's a home phone number, use the home phone.
- If there's no home phone number, use the mobile phone number.
- If there's no home or mobile phone number, use the work phone number.
- If there are no home, mobile, or work numbers, use a null value.
- String manipulation
- The following table includes some string manipulation examples:
Sample String Manipulation Expressions Description ${record:valueOrDefault('/Payment', 'unknown')} Replaces missing or null values in the Payment field with "unknown". ${str:toUpper(record:value('/STATE')} Capitalizes all strings in the STATE field. - Numeric operation
- The following table includes an example of a numeric operation:
Sample Numeric Operations ${record:value('/total_amount') - (record:value('/tip_amount') + record:value('/tolls') + record:value('/mta_tax'))} An expression that calculates trip revenue by subtracting the tip, taxes, and tolls from the total fare amount