Batch Case Study
Transformer can run pipelines in batch mode. A batch pipeline processes all available data in a single batch, and then stops.
A batch pipeline is typically used to process data that has already been stored over a period of time, often in a relational database or in a raw or staging area in a Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
Let's say that you have an existing data warehouse in a relational database. You need to
create a data mart for the sales team that includes a subset of the data warehouse
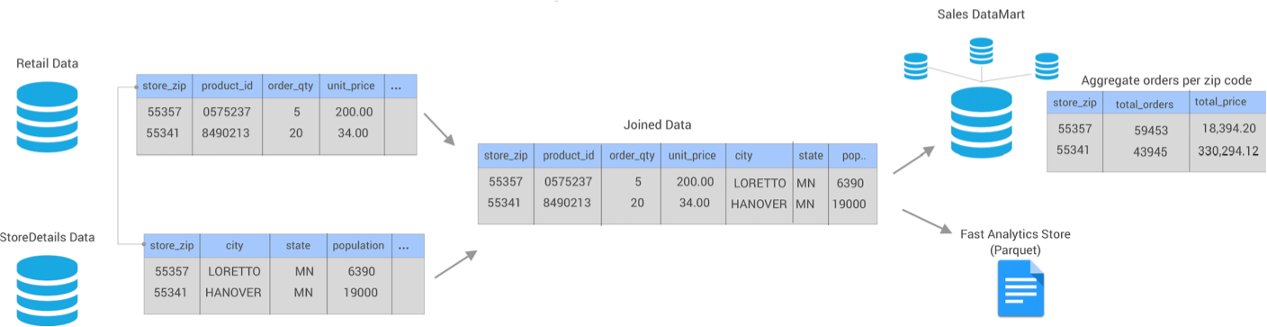
tables. To create the data mart, you need to join data from the Retail
and StoreDetails tables using the store zip code field. The
Retail table includes transactional data for each order, including
the product ID, unit price, store ID, and store zip code. The
StoreDetails table includes demographic data for each store zip
code, such as the city and population.
You also need to aggregate the data before sending it to the sales data mart to calculate the total revenue and total number of orders for each zip code.
In addition, you need to send the same joined data from the Retail and
StoreDetails tables to Parquet files so that data scientists can
efficiently analyze the data. To increase the analytics performance, you need to create
a surrogate key for the data and then write the data to a small set of Parquet
files.
The following image shows a high-level design of the data flow and some of the sample data:
You can use Transformer to create and run a single batch pipeline to meet all of these needs.
- Set execution mode to batch
- On the General tab of the pipeline, you set the execution mode to batch.
- Join data from two source tables
- You add two JDBC Table origins to the pipeline, configuring one to read from
the
Retaildatabase table and the other to read from theStoreDetailstable. You want both origins to read all rows in each table in a single batch, so you use the default value of -1 for the Max Rows per Batch property for the origins. - Aggregate data before writing to the data mart
- You create one pipeline branch that performs the processing needed for the sales data mart.
- Create a surrogate key and repartition the data before writing to Parquet files
- You create a second pipeline branch to perform the processing needed for the Parquet files used by data scientists.
The following image shows the complete design of this batch pipeline:
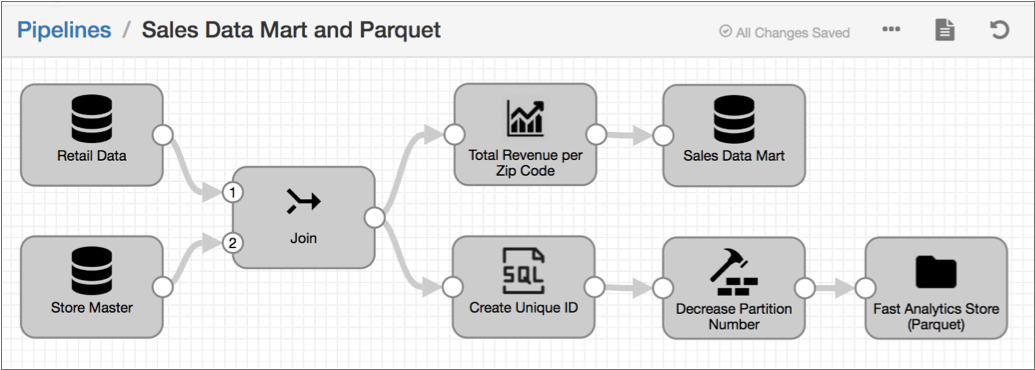
When you start this batch pipeline, the pipeline reads all available data in both database tables in a single batch. Each processor transforms the data, and then each destination writes the data to the data mart or to Parquet files. After processing all the data in a single batch, the pipeline stops.